Figure 4.
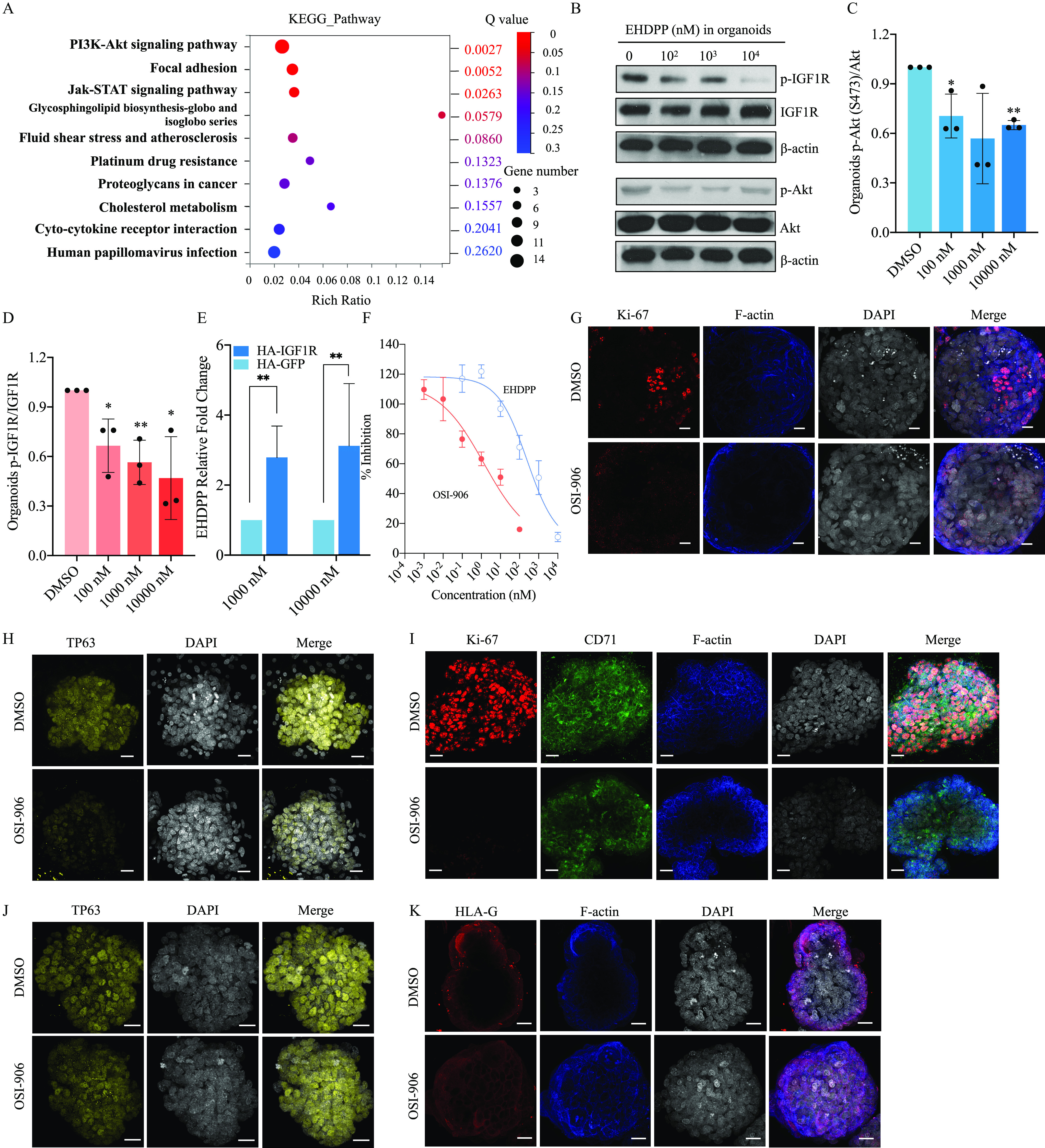
Investigating mechanisms of placentation disruption using organoids. (A) RNA-seq in Control and EHDPP () exposure groups in trophoblast organoids; (B) Protein levels of p-IGF1R (Y1135), IGF1R, p-Akt (S473), Akt and β-actin in control and EHDPP exposure groups in trophoblast organoids; (C) Relative protein level () of ; (D) Relative protein level () of ; (E) Relative binding affinity of EHDPP (); (F) In vitro kinase activity () of IGF1R of EHDPP and OSI-906 (); (G) Ki67 (red), F-actin (blue) and DAPI (gray) in control and 2-d OSI-906 () exposure groups; (H) TP63 (yellow) and DAPI (gray) in control and 2-d OSI-906 () exposure groups; (I) Ki67 (red), CD71 (green), F-actin (blue) and DAPI (gray) in control and 10-d OSI-906 () exposure groups; (J) TP63 (red) and DAPI (gray) in control and 10-d OSI-906 () exposure groups; (K) HLA-G (red), F-actin (blue) and DAPI (gray) in control and 10-d OSI-906 () exposure groups. Data in (C–F) are expressed relative to the levels in DMSO-treated organoids, which were set to 1. . All organoids in Figure 4 were from a single donor. Data were analyzed using an unpaired two-tailed Student’s -test. Indicated values are significantly different from the control value. Scale bars, . Numeric data in (C), (D) and (E) are listed in Table S12. Numeric data in (F) are listed in Table S13. Note: Akt, protein kinases B; CD71, transferrin receptor; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DMSO, dimethylsulfoxide; EHDPP, 2-ethylhexyl-diphenyl phosphate; HLA-G, human leukocyte antigen protein-G; IGF1R, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; OSI-906, linsitinib; RNA-seq, RNA sequencing; SD, standard deviation; TP63, tumor protein 63. *. **.
