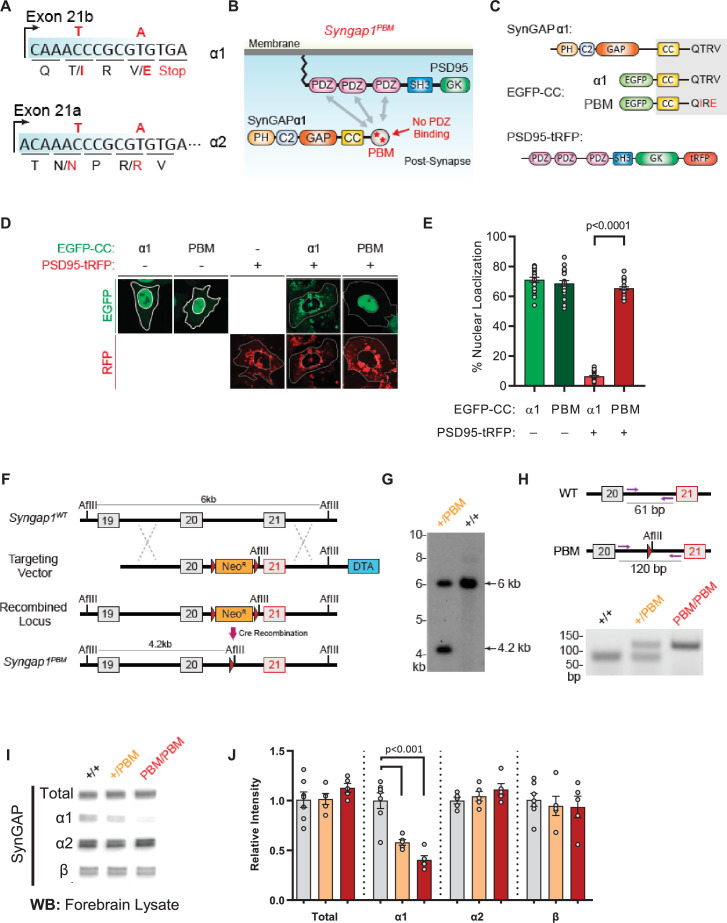
Figure 5. Validation of SynGAP PDZ binding motif (PBM) mutations and construction of the Syngap1PBM mouse line.
(A) Schematic diagram for exon map and alternative use of Exon21 in Syngap1 gene. Exon21b encodes for α1 isoform. Exon 21 a encodes for α2 isoform. Point mutations indicated in red alter exon 21b coding sequence without influencing exon21a open reading frame. (B) Schematics of SynGAPα1 and PSD95 domain structure and the location of point mutations. (C) Illustrations of constructs expressed in HeLa cells to study PDZ-dependent interaction between SynGAP and PSD95. EGFP-CC constructs are homologous to SynGAPα1 C-terminus. (D) Co-localization of EGFP-CCα1 and PSD95-tRFP in HeLa Cells. Representative images showing subcellular localizations of WT or PDZ-binding mutant (PBM) EGFP-CCα1 and PSD95-tRFP in HeLa cells when expressed individually or together. (E) Quantification of (D). Nuclear localization is calculated as the ratio of EGFP signal colocalized with DAPI vs total EGFP intensity in within an individual cell. ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, F(3, 96) = 531.4. p < 0.0001 (F) Schematics of the targeting strategy. The targeting vector was spanning Exon20 and 21. The vector included point mutations in Exon21, a neomycin resistance selection cassette flanked by Cre recombination sites and diphtheria toxin selection cassette (DTA). (G) Southern blot analysis showing the genomic DNA of the tested heterozygous mice compared to C57BL/6 J wild-type DNA. The AflII digested DNAs were blotted on nylon membrane and hybridized with external 5' probe spanning exon19. (H) PCR based genotyping strategy. Primers flanking leftover LoxP site yields 61 bp product in WT and 120 bp product in mutated allele. (I) Representative western blots showing expression levels of total SynGAP and individual isoforms in forebrain lysates. (J) Quantification of I. Relative intensity of bands normalized to total protein signal. Only α1 signal is significantly changed. ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, F(2, 14) = 24.86, n = 5.