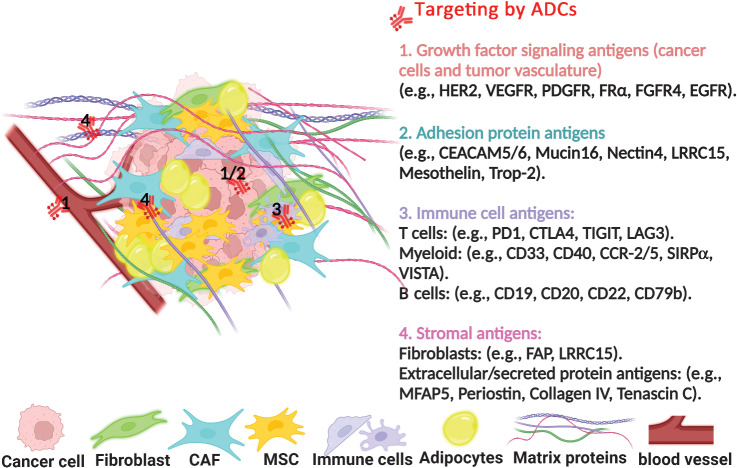
Figure 1.
Current development in targeting the tumor-stromal interaction by ADCs is being pursued preclinically and in early clinical trials to discover novel therapeutic interventions. PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; FRα, folate receptor α; CEACAM5/6, carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules; Trop-2, trophoblast cell surface antigen 2; CTLA4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4; TIGIT, T-cell immunoreceptor with immunoglobulin and ITIM domains; LAG3, lymphocyte activation gene-3; CD, cluster of differentiation; CCR-2/5, C-C chemokine receptor; SIRPα, signal regulatory protein α; VISTA, V-domain Ig suppressor of T-cell activation; FAP, fibroblast activation protein; MFAP5, microfibril associated protein 5.