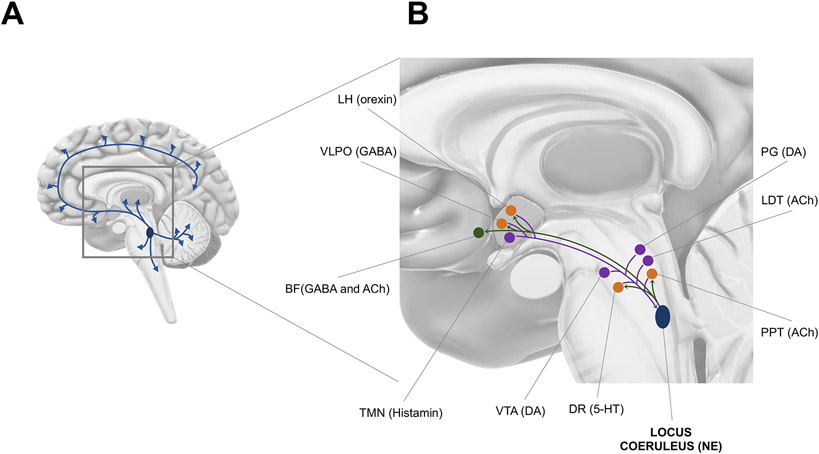
Fig. 1. Afferences and efferences of the brainstem locus coeruleus (LC).
(A) The LC sends ubiquitous projections over most of the brain including the hippocampus, amygdala, thalamus, and neocortex.
(B) Relationships between the LC and other sleep-wake
centers. Purple dots  represent nuclei which send projections to the LC; green dots
represent nuclei which send projections to the LC; green dots  represent nuclei which receive inputs
from the LC; orange dots
represent nuclei which receive inputs
from the LC; orange dots  represent nuclei which both send and receive projections from the LC. LC
efferences (
represent nuclei which both send and receive projections from the LC. LC
efferences ( ) target
cholinergic and GABAergic neurons of the basal forebrain (BF), GABAergic neurons
of the ventrolateral preoptic area (VLPO) in the anterior hypothalamus,
orexinergic neurons of the lateral hypothalamus (LH), serotoninergic neurons of
the dorsal raphe (DR), and cholinergic neurons of the pedunculopontine tegmentum
(PPT) nucleus. LC afferences (
) target
cholinergic and GABAergic neurons of the basal forebrain (BF), GABAergic neurons
of the ventrolateral preoptic area (VLPO) in the anterior hypothalamus,
orexinergic neurons of the lateral hypothalamus (LH), serotoninergic neurons of
the dorsal raphe (DR), and cholinergic neurons of the pedunculopontine tegmentum
(PPT) nucleus. LC afferences (  ) arise from orexinergic neurons of the lateral hypothalamus (LH), GABAergic
neurons of the VLPO, histaminergic neurons of the tuberomammillary nucleus
(TMN), dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area (VTA), serotoninergic
neurons of the dorsal raphe (DR), cholinergic neurons of the pedunculopontine
tegmentum (PPT) and laterodorsal tegmentum (LDT), and dopaminergic neurons of
the periaqueductal grey matter (PG). All nuclei are positioned for illustrative
purpose and may not reflect their precise anatomical location. 5-HT=serotonin;
ACh=acetylcholine; BF=basal forebrain; DA=dopamine; DR=dorsal raphe; LC=locus
coeruleus; LDT=laterodorsal tegmentum; LH=lateral hypothalamus;
NE=norepinephrine; PG=periaqueductal grey matter; PPT=pedunculopontine
tegmentum; TMN=tuberomammillary nucleus; VLPO=ventrolateral preoptic area;
VTA=ventral tegmental area.
) arise from orexinergic neurons of the lateral hypothalamus (LH), GABAergic
neurons of the VLPO, histaminergic neurons of the tuberomammillary nucleus
(TMN), dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area (VTA), serotoninergic
neurons of the dorsal raphe (DR), cholinergic neurons of the pedunculopontine
tegmentum (PPT) and laterodorsal tegmentum (LDT), and dopaminergic neurons of
the periaqueductal grey matter (PG). All nuclei are positioned for illustrative
purpose and may not reflect their precise anatomical location. 5-HT=serotonin;
ACh=acetylcholine; BF=basal forebrain; DA=dopamine; DR=dorsal raphe; LC=locus
coeruleus; LDT=laterodorsal tegmentum; LH=lateral hypothalamus;
NE=norepinephrine; PG=periaqueductal grey matter; PPT=pedunculopontine
tegmentum; TMN=tuberomammillary nucleus; VLPO=ventrolateral preoptic area;
VTA=ventral tegmental area.