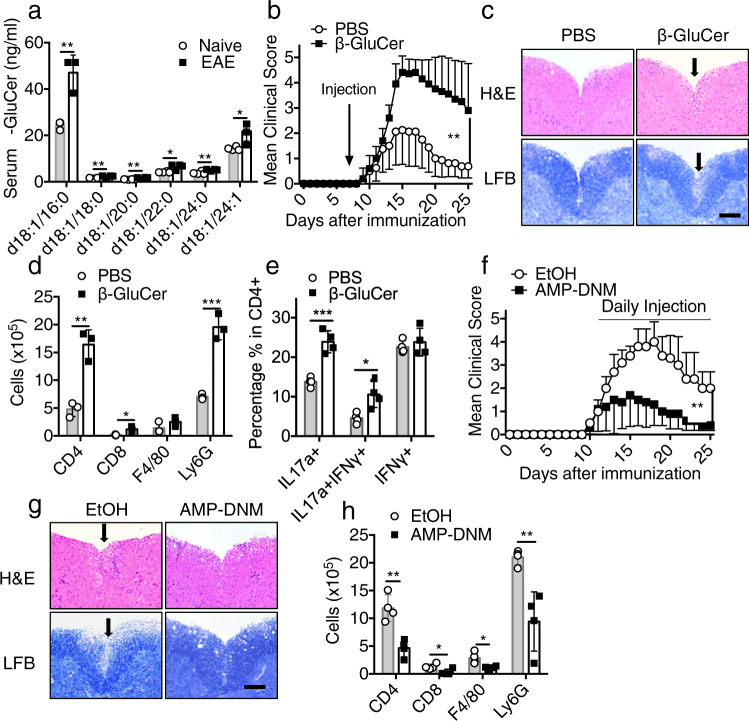
Fig. 6. β-Glucosylceramide administration promotes EAE.
a Quantification of β-glucosylceramide derivatives obtained from the serum of naive and EAE mice at the peak of the disease, n = 4 biological replicates. b EAE clinical scores of wild-type mice treated with synthetic β-glucosylceramide (150 μg/mice) or vehicle (PBS) on day 10 after EAE induction, n = 5 mice. c Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining (upper panels) and Luxol fast blue staining (lower panels) of lumbar spinal cords EAE mice harvested at the peak of disease. Scale bar, 100 μm. Arrows in the upper panel indicate inflammatory cells infiltration, and arrows in the lower panel indicate demyelination area. Representative data are shown for n = 4. d Absolute numbers of CNS-infiltrating cells were measured at the peak of disease by flow cytometry with indicated antibodies, n = 3 biological replicates. e Flow cytometry analysis of CD4+ lymphocytes from the brain of EAE mice at the peak of the disease, n = 4 biological replicates. f EAE clinical score of wild-type mice treated with AMP-DNM (25 mg/kg) or vehicle (EtOH) since the start of EAE symptom, n = 5 mice. g Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining (upper panels) and Luxol fast blue staining (lower panels) of lumbar spinal cords from EAE mice harvested at the peak of disease. Scale bar, 100 μm. Arrows in the upper panel indicate inflammatory cells infiltration, and arrows in the lower panel indicate demyelination area. Representative data are shown for n = 4. h Absolute numbers of CNS-infiltrating cells were measured at the peak of disease by flow cytometry with the indicated antibodies, n = 4 biological replicates. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (Two-sided student’s t test for a, d, e, h). **P < 0.01 (two-way ANOVA, b, d). Data are represented as mean ± SD. Exact P values for asterisks (from left to right): a 0.0016 0.0061 0.0178 0.0103 0.0129 b < 0.0001 d 0.0024 0.0144 0.0007 e 0.00056 0.01513 f 0.0033 h 0.0023 0.0323 0.0177 0.0057.