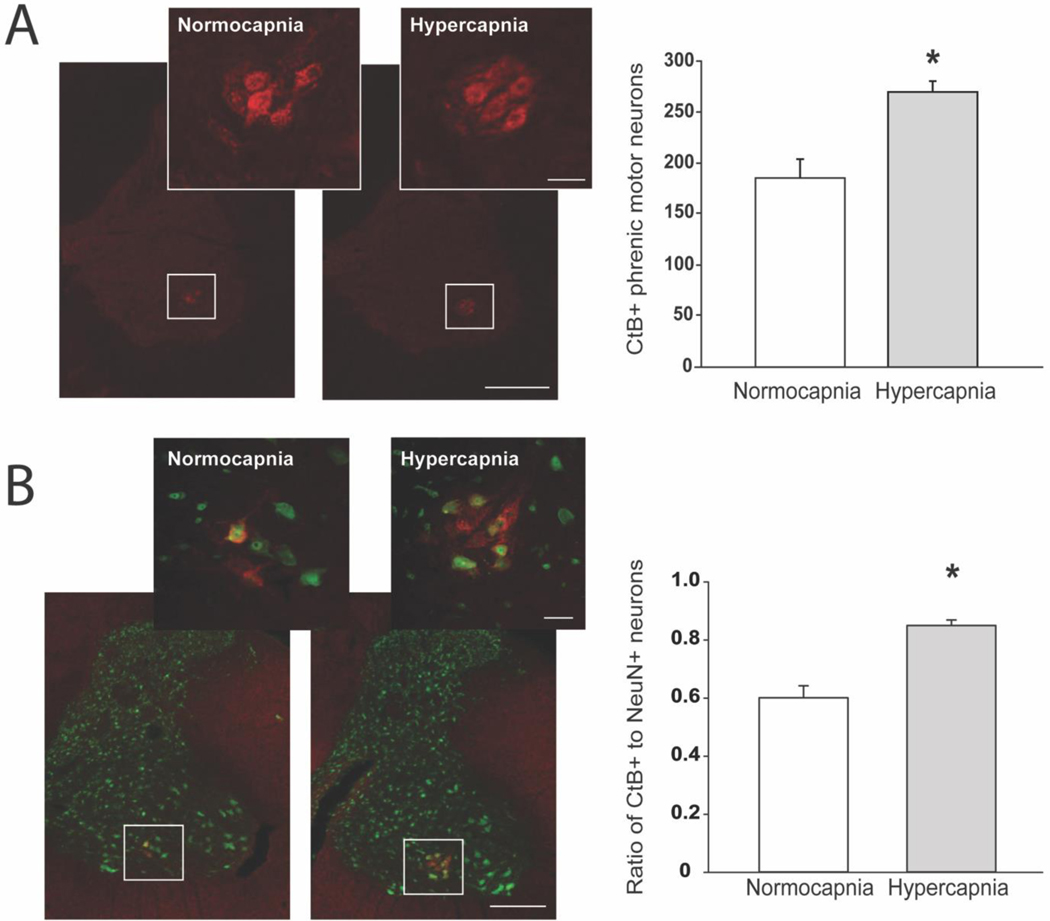
Figure 2. Validation of Modified Intrapleural Injection Methods to Optimize Retrograde Labeling of Phrenic Motor Neurons with Cholera toxin B.
In preliminary experiments, we validated improved intrapleural CtB tracing methods in spinal intact rats by comparing phrenic motor neuron labelling after injections delivered under isoflurane anesthesia with either poikilocapnic (n=7; FICO2=0%, FIO2=100%; white bars) or hypercapnic conditions (n=7; FICO2=7.1%, FIO2=20.8%, balanced N2; gray bars) using previously published methods (Nichols et al., 2013; Nichols et al., 2017; Nichols et al., 2015a). Briefly, transverse sections from the C4 spinal cord were dual labeled for CtB and NeuN. Tissues were incubated in primary antibodies (goat anti-CtB (1:2000); mouse anti-NeuN (1:500)) overnight at 4°C, followed by secondary antibodies (Alexa Fluor® 594 (donkey anti-goat 594; 1:1000); 488 (donkey anti-mouse 488; 1:1000) for 2 hours at room temperature. The total number of phrenic motor neurons within the C4 region was extrapolated from manual phrenic motor neuron cell counts from six C4 sections per animal (left and right phrenic motor neuron counts were not different from each other, and thus were averaged together for each section for extrapolation); briefly, we divided the total C4 segment length (2000 μm) by the thickness of each section (40 μm), and multiplied by the average number of phrenic motor neurons per animal. A. Representative images depict CtB labeling in the cervical spinal ventral horn from isoflurane anesthetized normocapnia and hypercapnia treated rats. (4x with a 20x inset of the phrenic motor pool; Scale bar at 4x = 400μm, 20x = 50μm. We observed increased CtB-labelling with injections performed under hypercapnia vs. normocapnia (*p<0.001). B. Tissue sections from these preliminary studies were also dual labeled with NeuN and manually counted by a blinded observer. The number of large, NeuN-labelled neurons was not different between groups (normocapnia: 307±13, hypercapnia: 320±18; data not shown). Thus, the ratio of CtB-labelled to NeuN-labelled cells was increased by hypercapnia (normocapnia: 0.60±0.04; hypercapnia 0.85±0.02; p<0.001), suggesting improved CtB labelling efficiency of phrenic motor neurons. Data were analyzed using Student’s t test. Differences were considered significant if p< 0.05. Data are displayed as mean±SEM.