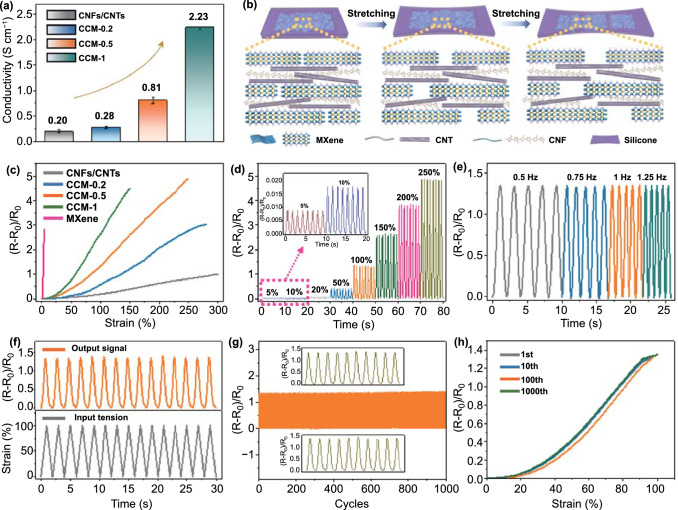
Fig. 3.
Electromechanical properties of CCM e-skin and mechanisms. a The electrical conductivity of the CCM e-skin at various MXene loadings. b Schematic diagram of the mechanism of the electromechanical responses of CCM e-skin. c Relative resistance changes of the CNFs/CNTs, CCM-0.2, CCM-0.5, CCM-1, and pristine MXene e-skin at different strains. d Relative resistance changes under various maximum stretching strains (5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 150, 200, and 250%) for the CCM-0.5 e-skin. e Relative resistance variation of the CCM-0.5 e-skin at different frequencies under 100% strain. f Time retention curves of the variation in resistance and strain with time. g Relative resistance change of the CCM-0.5 e-skin during 1000 cycles of stretching/relaxing between 0 and 100% strain at a constant frequency of 1 Hz. h Resistance variation for multiple-cycle tests: 1st (gray), 10th (blue), 100th (orange), and 1000th (green) cycles under 100% strain