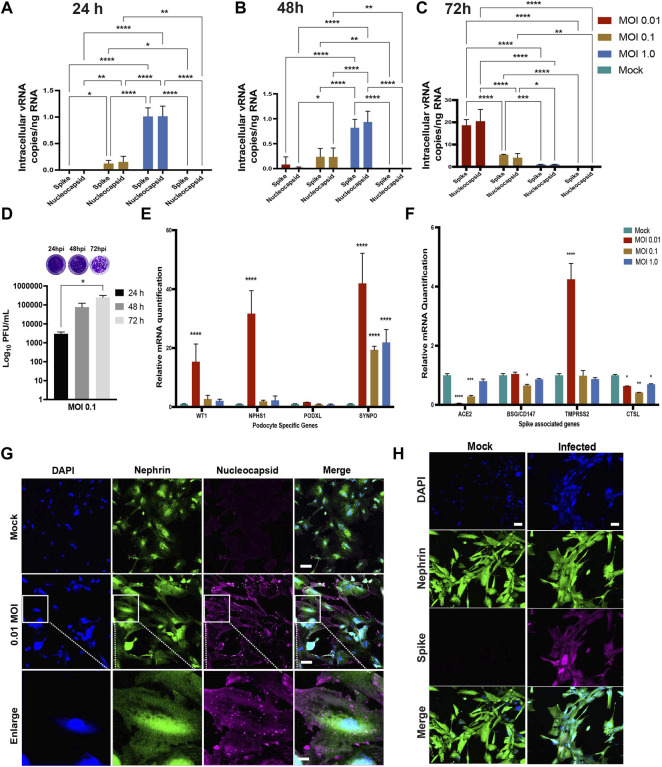
FIGURE 3.
Susceptibility of human iPS cell-derived podocytes to infection by live SARS-CoV-2. qPCR analysis of human iPS cell-derived podocytes infected with SARS-CoV-2 revealed intracellular uptake of the virus for 24 h.p.i (A), 48 h.p.i (B) and 72 h.p.i (C). (D) plaque assay quantification from supernatant obtained from infected podocytes at 24, 48 and 72 h.p.i. (E) qPCR analysis of podocyte-specific genes revealed that both synaptopodin (SYNPO) and podocalyxin (PODXL) are significantly upregulated after infection with SARS-CoV-2 at MOI of 0.01, whereas SYNPO is significantly upregulated at multiple MOIs, and PODXL shows no significant changes with viral infection. (F) The expression of spike-associated genes (ACE2, BSG/CD147) and spike processing genes (TMPRSS2, CTSL) are significantly impacted by infection at MOIs of 0.01 and 0.1, respectively. (G) Human iPS cell-derived podocytes treated with SARS-CoV-2 (at MOI of 0.01) immunostain positive for Nucleocapsid protein (magenta), indicating successful infection with the virus. The cells were immunostained also for the podocyte marker Nephrin (green) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 100 µm (H) Spike positive cells Nephrin and DAPI as nuclear counterstain in the infected podocytes. Scale bar: 100 µm. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Sidak’s multiple comparison test was used to determine statistical significance. Only p values of 0.05 or lower were considered statistically significant (p > 0.05 [ns, not significant], p < 0.05 [*], p < 0.01 [**], p < 0.001 [***], p < 0.0001 [****]). Error bars indicate standard deviation of the mean.