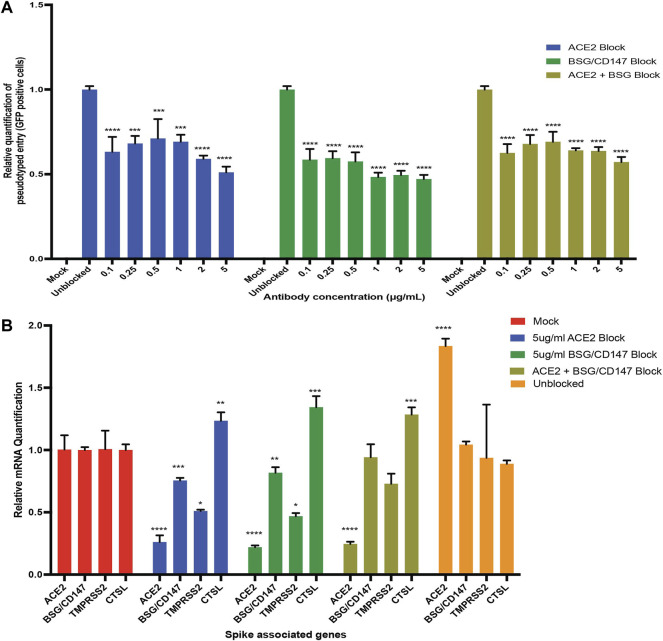
FIGURE 5.
Antibody blocking reveal roles of ACE2 and BSG/CD147 receptors in viral uptake. (A) qPCR quantification of S-pseudotyped entry relative to antibody concentration (normalized to unblocked samples). Human iPS cell-derived podocytes were incubated with different dilutions of anti-ACE2, anti-BSG or both for an hour followed by infection with S-pseudotyped virus at MOI 0.02 for 60 h (B) qPCR quantification of Spike binding receptor genes (ACE2, BSG/CD147) and Spike processing factor genes (TMPRSS2, CTSL) at 5 µg/ml for both anti-ACE2 antibody blockage and anti-BSG antibody blockage showing significant changes in gene expression with optimal receptor blockage when compared to unblocked samples (normalized to mock groups). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Sidak’s multiple comparison test was used to determine statistical significance. Only p values of 0.05 or lower were considered statistically significant (p > 0.05 [ns, not significant], p < 0.05 [*], p < 0.01 [**], p < 0.001 [***], p < 0.0001 [****]). Error bars indicate standard deviation of the mean.