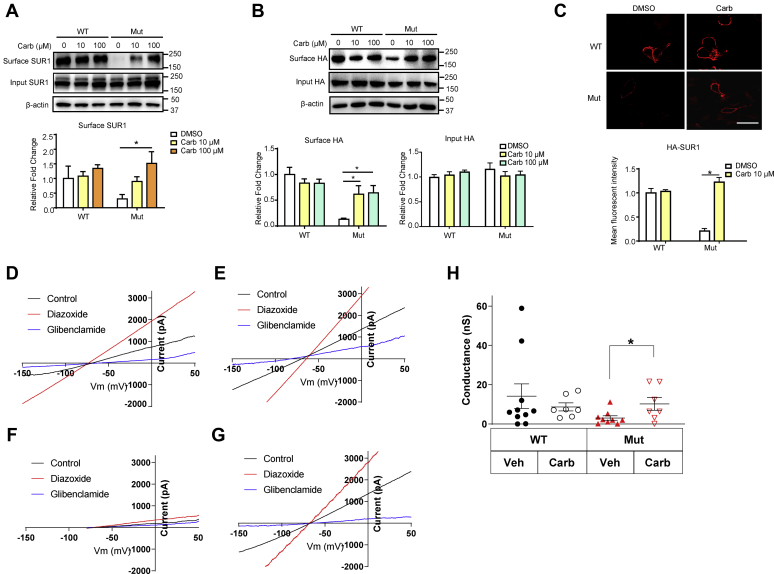
Figure 2.
Carbamazepine (Carb) increases surface SUR1 expression in INS-1 cells expressing mutant KATPchannels.A, top, representative blotting images show the surface biotinylation of SUR1 in INS-1 cells expressing WT (HA-SUR1/Kir6.2) or mutant (HA-SUR1/Kir6.2-A28V) KATP channels, after treatment with 10 μM or 100 μM Carb for 16 h. Bottom, quantification of surface SUR1 is shown in the plot. B, top, representative blotting images show the surface biotinylation of HA epitope in INS-1 cells expressing WT or mutant KATP channels after treatment with 10 μM or 100 μM Carb for 16 h. Bottom, quantification of surface and input HA epitope were shown in the plots separately. C, top, representative immunostaining images showed surface staining of HA-tagged WT and mutant KATP channels in INS-1 cells. Bottom, the bar graph shows the fluorescence intensity of the HA signal. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM; n = 8 per group; ∗p < 0.05, compared with the DMSO-treated cells in each corresponding group; differences were evaluated using two-way ANOVA and Dunnett's post hoc test. The scale bar represents 10 μm. D, representative WT KATP currents (black) elicited by a voltage ramp (0.5 V/s). The KATP currents were activated by 300 μM KATP channel opener diazoxide (red) and inhibited by 10 μM KATP channel blocker glibenclamide (blue). E, representative WT KATP currents from a HEK293 cell treated with 10 μM Carb overnight. F, representative Kir6.2 A28V KATP currents from a HEK293 cell treated with vehicle control. G, representative Kir6.2 A28V KATP currents from a HEK293 cell treated with 10 μM Carb overnight. H, summary of WT and Kir6.2 A28V KATP currents in HEK cells treated with either vehicle control or 10 μM Carb overnight. This overnight Carb treatment significantly augmented the whole-cell Kir6.2 A28V KATP currents (t test, ∗p < 0.05). DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; HA, hemagglutinin; HEK293, human embryonic kidney 293 cell line; KATP, ATP-sensitive potassium channel; SUR1, sulfonylurea receptor 1.