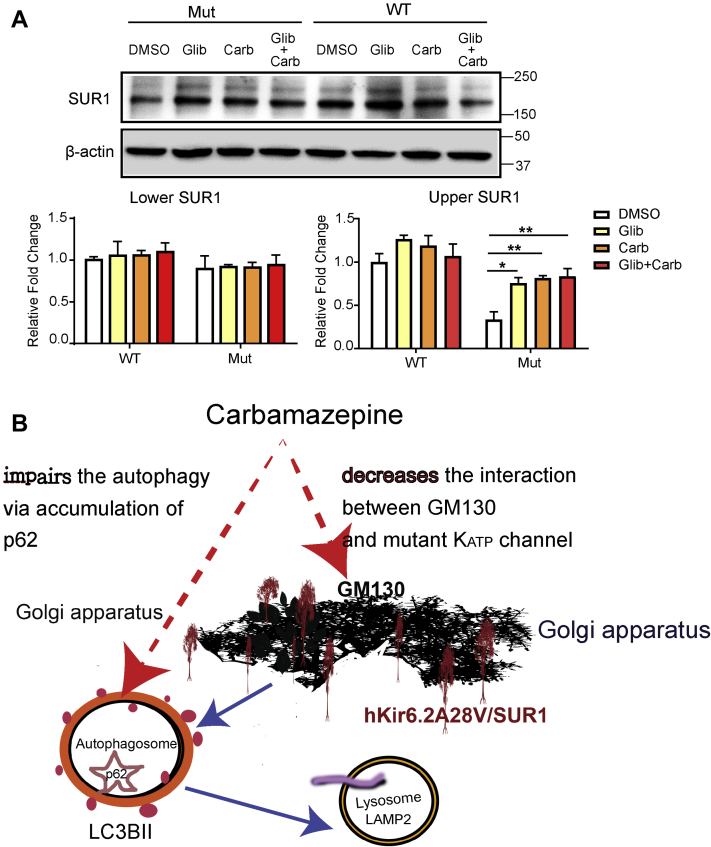
Figure 9.
Carbamazepine (Carb) and sulphonylureas share the same binding site on SUR1.A, top, representative immunoblots for SUR1 in INS-1 cells expressing WT (HA-SUR1/Kir6.2) or mutant (HA-SUR1/Kir6.2-A28V) KATP channels, upon treatment with DMSO, 10 μM Glib, or 10 μM Carb +10 μM Glib for 16 h. Bottom, quantification of the upper (mature) and lower bands of SUR1 is shown in the left and right plots, respectively. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM; n = 5 per group; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001, compared with DMSO-treated cells in each corresponding group; differences were evaluated using two-way ANOVA and Dunnett's post hoc test. B, summary of Carb rescue of mutant KATP channel trafficking via two pathways. First, Carb decreases the interaction of mutant KATP channels with the Golgi matrix protein, GM130, allowing the mutant channels to reach the cell surface. Second, Carb attenuates autophagy-dependent protein degradation (indicated by accumulation of p62), which allows mutant KATP channels to pass through the ER. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; HA, hemagglutinin; KATP, ATP-sensitive potassium channel; SUR1, sulfonylurea receptor 1.