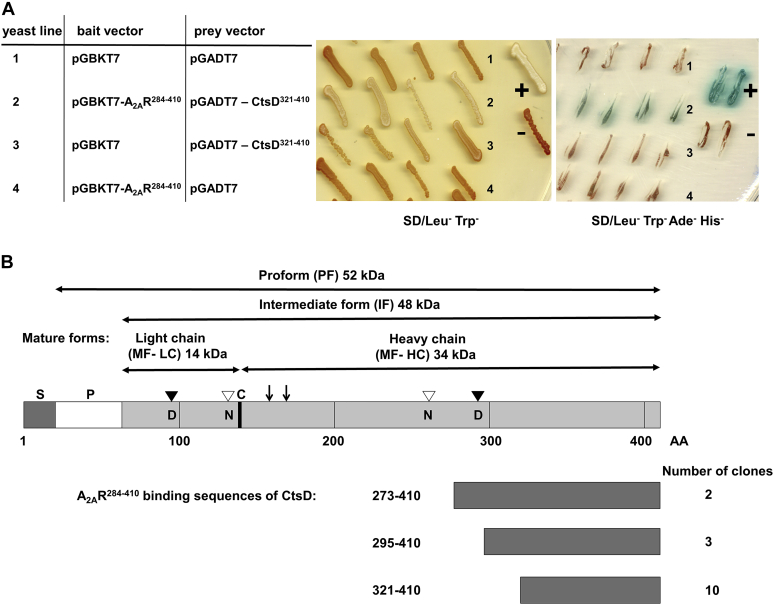
Figure 1.
Validation of the interaction between CtsD and the A2AR C-terminal tail in yeast.A, transformation of Yeast 2H Gold strain with pGBKT7, pGBKT7-A2AR284–410 (bait), pGADT7 and pGADT7-CtsD321–410 (prey) vectors in a pairwise combination, according to the numbered yeast line. The yeast cells were grown on SD/Leu− Trp− or SD/Leu− Trp− Ade− His− (in the presence of Aureobasidin and X-α-Gal) selective medium. pGBKT7-p53 and pGADT7-SV40 small T antigen were used as positive controls and pGBKT7-p53 and pGADT7-Lamin expressing vectors were used as negative controls. B, presentation of the different maturation forms of CtsD. Characterization of A2AR284–410 interactor clones that encode the different ORFs of the CtsD. The amino acid numbers of pre–pro-CtsD protein (P18242) is based on UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot databases. S: N-terminal secretion signal peptide (20 amino acids [AA]); P: propeptide (44 AA); C: cleavage site between the light and heavy chain of CtsD; arrows indicate the processing sites; D: catalytic Asp residues (D97 and D295) are depicted by black triangles; N: N-linked glycosylation sites at Asn residues (N134 and N261) are depicted by empty triangles (26). A2AR, adenosine A2A receptor; CtsD, cathepsin D.