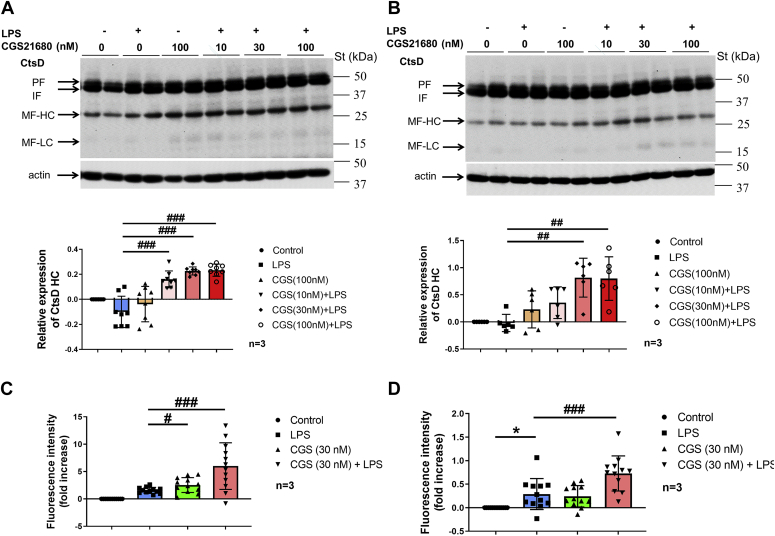
Figure 6.
A2AR activation increases the maturation and enzyme activity of CtsD in macrophages.A, protein samples were isolated from RAW 264.7 cells after LPS activation and treatment with the A2AR agonist CGS21680. B, protein samples were isolated from mouse IPMΦ cells after the same treatment as in A. About 10 μg of total protein sample in each lane were analyzed in duplicate by WB using CtsD-specific polyclonal antibody. Sample loading was normalized for β-actin. Statistical analyses of the relative expression of CtsD heavy chain (HC) are based on three independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Values from ANOVA: F = 9.641 and p < 0.001 for IPMΦ and F = 22.91 and p < 0.001 for RAW 264.7 cells. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus LPS-activated cells. C, secreted and D, cytosolic aspartyl protease–specific activity of A2AR agonist-treated LPS-activated IPMΦ cells. Statistical evaluation of aspartyl protease–specific activity is based on three independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Values from ANOVA: F = 15.34 and p < 0.001 for secreted and F = 14.74 and p < 0.001 for cytosolic aspartyl protease–specific activity. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus control (vehicle treated); ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 versus LPS-activated cells. A2AR, adenosine A2A receptor; CtsD, cathepsin D; IPMΦ, mouse peritoneal macrophage; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; WB, Western blot.