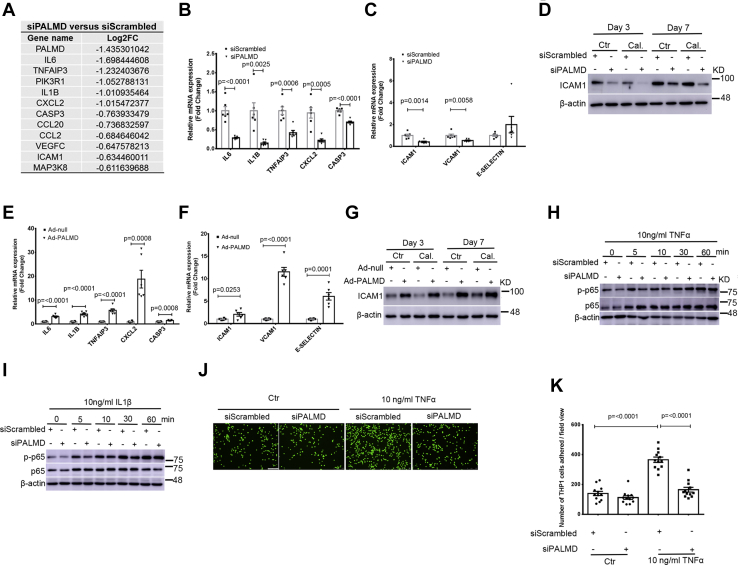
Figure 5.
PALMD regulates PFKFB3 and NF-κB–mediated inflammation in hVICs. hVICs were transfected with 20 nM siScrambled or siPALMD and treated with control medium (Ctr) or calcifying medium (Cal.) for 48 h. A, selected NF-κB target genes regulated by PALMD in hVICs revealed by RNA-Seq. B, validation of NF-κB target genes revealed by RNA-Seq in hVICs with PALMD depletion at 48 h using RT-qPCR including IL6, IL1B, TNFAIP3, CXCL2, and CASP3, n = 6. C, RT-qPCR showing mRNA expression of the adhesion molecule ICAM1, VCAM1, and E-SELECTIN in hVICs with depleted PALMD at 48 h, n = 6. D, representative Western blotting images for ICAM1 and β-actin protein expression in hVICs with depleted PALMD at day3 and day 7, n = 5. E, RT-qPCR showing the TNFα–NF-κB signaling-relevant genes in hVICs with PALMD overexpression at 48 h, n = 6. F, RT-qPCR showing mRNA expression of ICAM1, VCAM1, and E-SELECTIN in hVICs with PALMD overexpression at 48 h, n = 6. G, representative Western blotting images for ICAM1 and β-actin protein expression in hVICs with PALMD overexpression at day3 and day 7, n = 3. H and I, hVICs with depleted PALMD expression were treated with 10 ng/ml TNFα or IL1β at the indicated time. Representative Western blotting images for p-p65, p65, and β-actin protein expression, n = 4. J, representative fluorescence microscopic images of the calcein-AM labeled THP1 cells that adhered to hVICs with depleted PALMD expression. The scale bar represents 100 μm. K, quantitative assay of the THP1 cells that adhered to hVICs with depleted PALMD expression, n = 12. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, and statistical significance was analyzed by a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. hVIC, human valve interstitial cell; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB.