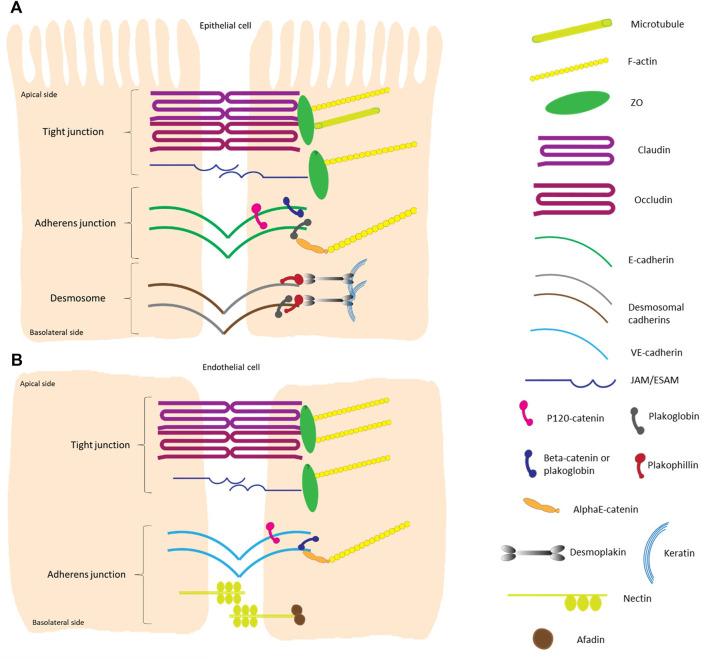
FIGURE 2.
Schematic overview of the different components of intercellular junctions in epithelial and endothelial cells. (A) Highly polarized epithelial cell-cell contacts are composed of tight junctions, adherens junctions and desmosomes from the apical to basal side. The transmembrane proteins of tight junctions are claudins, which largely determine the paracellular ion permeability between cells, and proteins like occludin and junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs) (Zihni et al., 2016; Otani and Furuse, 2020). The cytosolic plaque of the tight junctions is a complex protein network, with adaptor proteins containing multiple protein-protein interaction motifs that are connected to F-actin and microtubules. One of the main cytoplasmic tight junction proteins are of the zonula occludens (ZO) family. Adherens junctions consist of transmembrane cadherin proteins, such as E-cadherin, and cytoplasmic proteins that are members of the catenin family; p120-catenin binds to E-cadherin closest to the intercellular space while α-catenins anchor the cadherin-catenin complex to the actin cytoskeleton by binding to the armadillo proteins β-catenin and/or plakoglobin (Gumbiner 2005; Perez-Moreno and Fuchs, 2006; Meng and Takeichi, 2009). The main transmembrane proteins in the desmosomal complex are two types of cadherins: desmogleins and desmocollins. They form heterodimers that make up the fundamental adhesive unit of desmosomes (Harrison et al., 2011). The cytoplasmic side of the desmosomal cadherins are linked with plakophilin and plakoglobin, which in their turn bind both to desmoplakin to make up the connection to the intermediate filament (keratin) complex of the cell (Green and Gaudry, 2000; Garrod and Chidgey, 2008). (B) Tight junctions in flat endothelial cells are very similar to those in polarized epithelial cells. The major difference is that there is no microtubule to bind to in the endothelial cells. Adherens junctions consist of vascular endothelial cadherin (vascular-endothelial) in endothelial cells and do not contain plakoglobin as cytoplasmic protein. Transmembrane nectin protein attached to the cytoplasmic afadin can be found in endothelial cells (Wallez and Huber, 2008). The overall height of a polarized cell grown in vitro is ∼15 μm, figures are not on scale.