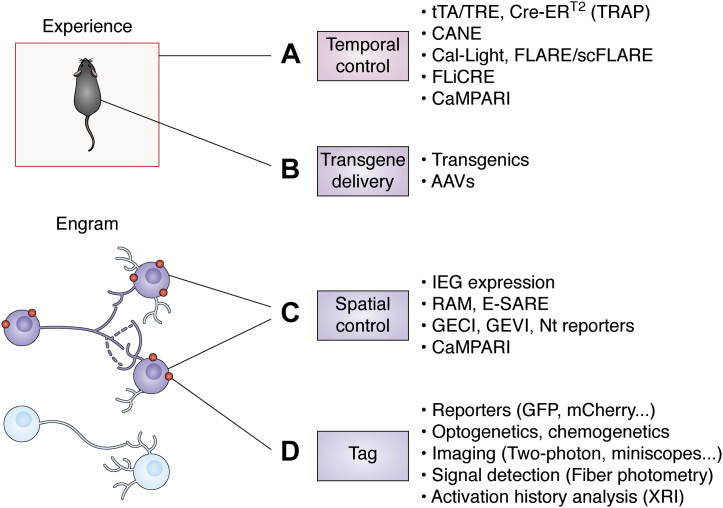
Figure 2.
The expanded engram toolbox. Engram cell tagging has been achieved with several strategies or tools that can be used individually or combined. A, temporal control allows labeling engrams responsible for encoding a particular experience and can be achieved with different strategies. The tTA/TRE or Cre-ERT2 (targeted recombination in active populations [TRAP]) genetic strategies are temporally controlled by the delivery of doxycycline or tamoxifen, respectively. The capturing activated neuronal ensembles (CANE) technology allows high temporal precision by engineering viruses to specifically infect activated neurons. Other tools (Cal-Light, Fast light–regulated and activity-regulated expression [FLARE] and its improved version single-chain FLARE [scFLARE], and fast light–regulated and calcium-regulated expression [FLiCRE]) rely on the combination of two requirements to achieve temporal control: increase in intracellular Ca2+ and delivery of light. A similar strategy based on the coincidence of activity and light is used by CaMPARI to label only activated cells. B, transgenes can be delivered by generating transgenic mice models or by the use of vectors such as adeno-associated viruses (AAVs). C, only activated cells (engram cells, purple) are tagged; thanks to several spatial control strategies. The expression of immediate early genes (IEGs) such as c-fos can be used to manipulate only activated cells. Engineered artificial promoters have been also used in the robust activity marking (RAM) or the enhanced synaptic activity–regulated element (E-SARE) systems. Intracellular Ca2+ levels are detected by genetically encoded calcium or voltage indicators (GECI and GEVI, respectively) as well as reporters that detect specific neurotransmitter (Nt) release. CaMPARI is a fluorescent indicator that responds to intracellular Ca2+ levels. D, engram cells can be tagged with reporters (e.g., GFP or mCherry fluorescent reporters). They can also be tagged with tools that will allow future manipulation by light (optogenetics) or by drugs (chemogenetics). They can be imaged with several techniques such as two-photon or head-mounted miniature microscopes (miniscopes). Their activity can be monitored by techniques that allow activity readings such as fiber photometry. Activation history over time can be investigated by the use of the expression recording island (XRI) technology. CaMPARI, calcium-modulated photoactivatable ratiometric integrator; GECI, genetically encoded calcium indicator; GEVI, genetically encoded voltage indicator; tTA, tetracycline transactivator.