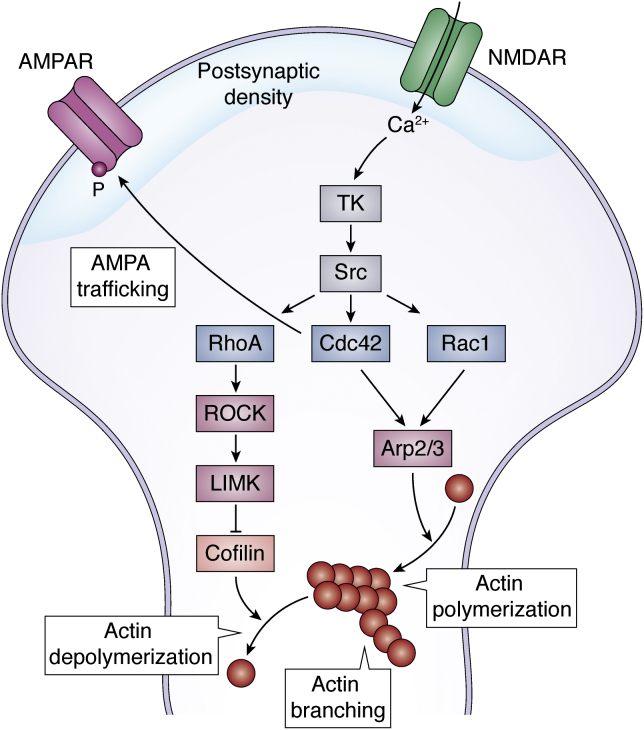
Figure 4.
Cytoskeletal modifications after learning. The increase in intracellular Ca2+ provoked by neuronal activation activates tyrosin kinases (TKs) and Src kinases. These activate members of the Rho family small GTPases: RhoA, Cdc42, and Rac1. RhoA activates ROCK and subsequently LIMK kinases, which in turn inhibits effector cofilin and eventually inhibits actin depolymerization. Rac1 and Cdc42 activate Arp2/3, an actin nucleation factor that induces actin polymerization, the elongation of actin filaments, and actin branching, and the formation of new ramifications in the actin filaments. Rho GTPases also anchor, stabilize, phosphorylate, and insert AMPARs to the postsynaptic density area of the membrane. AMPAR, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptor; LIMK, LIM-domain kinases; NMDAR, N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor; Rac1, Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1; RhoA, Ras homologous member A; ROCK, Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase.