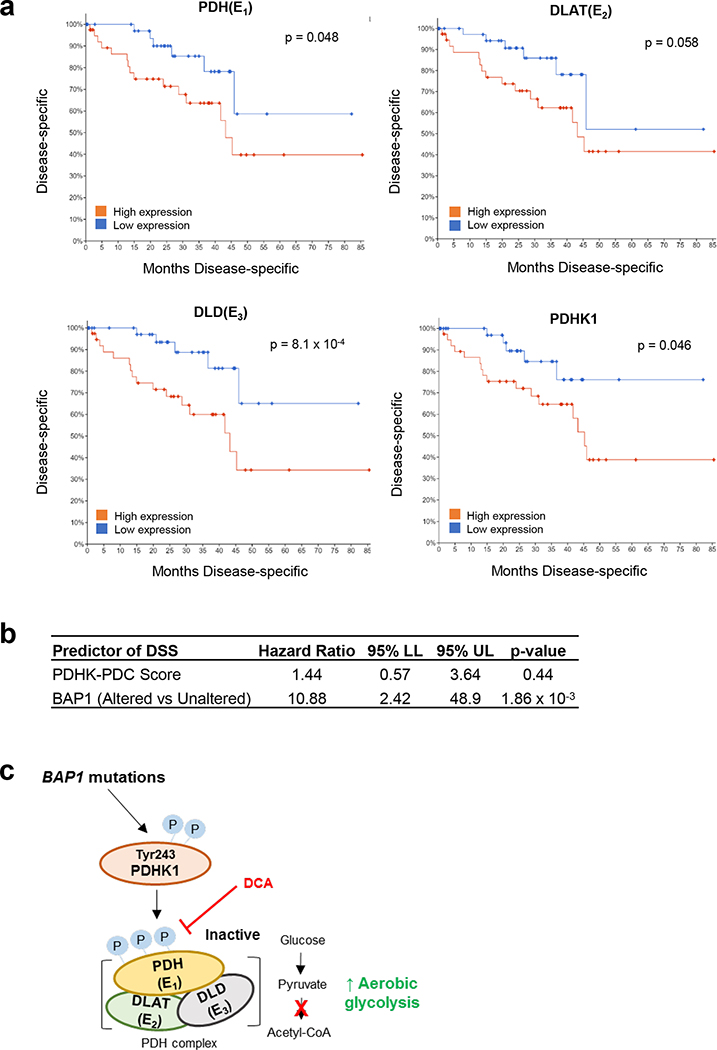
Figure 7. UM patient survival curve based on PDC and PDHK1 expression.
a. Analysis of TCGA data retrieved from the TCGA Pan-Cancer Clinical Data Resource (TCGA-CDR) for UM patient disease specific survival based on PDH (E1), DLAT (E2), DLD (E3) and PDHK1 expression are shown. Expression is stratified into high (n=40) or low (n=40) by median expression of each gene. Logrank test was used to determine significance in overall survival (https://wiki.nci.nih.gov/plugins/servlet/mobile#content/view/24279961). b. Cox proportional hazards (PH) model analysis for the association between disease-specific survival, PDHK-PDC score and BAP1 alteration status are shown. Patients were stratified into BAP1 altered groups based on BAP1 mutation and copy loss data. PDHK-PDC scores were calculated by averaging the z-score value for PDH, DLAT, DLD and PDHK1. c. A summary mechanism of BAP1 mutant-driven glycolysis in UM. BAP1 mutations induces phosphorylation of PDHK1-PDH axis, elevating aerobic glucose utilization of BAP1 mutant UM cells. Inhibition of PDH phosphorylation reduces BAP1 mutant UM cell growth via cell cycle arrest.