Figure 1. Eligibility, Randomization, and Data Availability in a Trial of Self-monitoring for Blood Pressure Control in Pregnant Individuals With Hypertension.
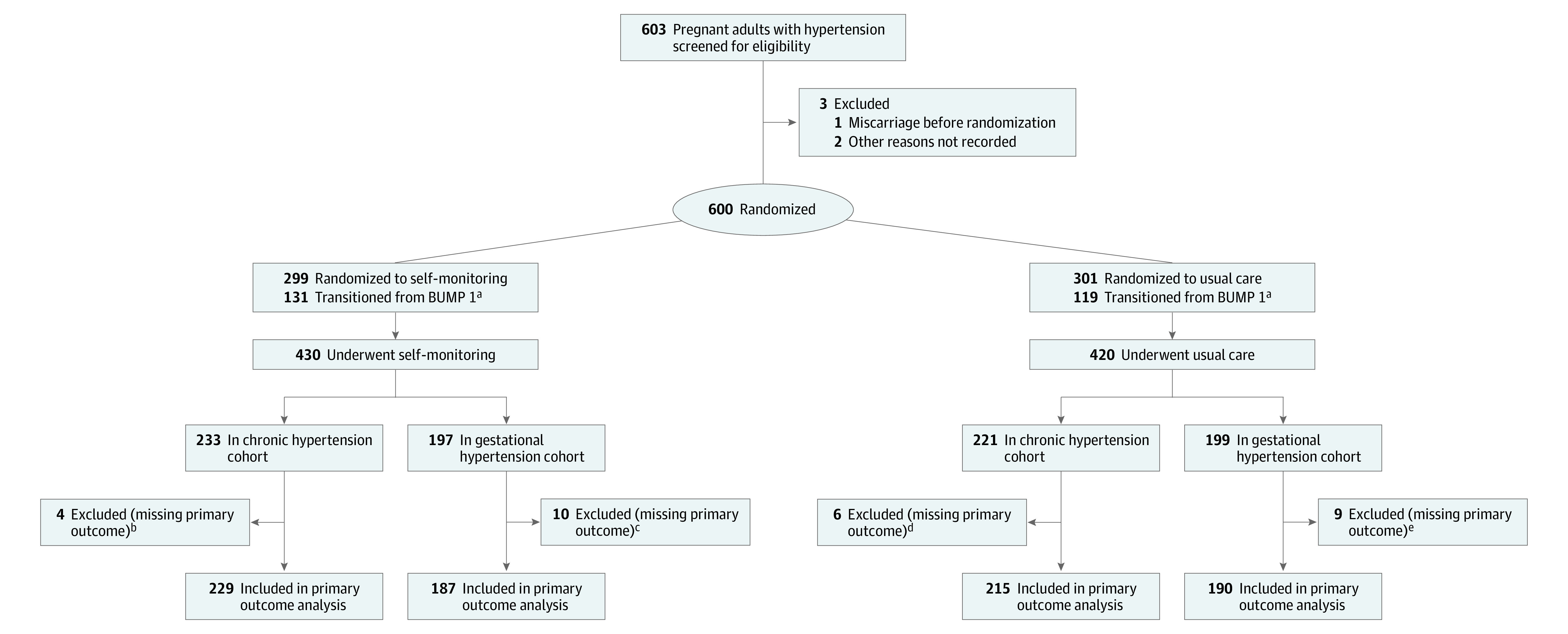
aThe BUMP 1 trial aimed to establish whether self-monitoring blood pressure with telemonitoring in addition to usual care could lead to earlier detection of elevated clinic blood pressure, compared with usual care, during higher-risk pregnancies. A total of 250 pregnant individuals who developed gestational hypertension during the linked BUMP 1 trial migrated to this trial, staying in their original randomization groups but changing to daily monitoring.
bDelivery date not recorded so primary outcome could not be determined (n = 2); delivery more than 2 days after entering the trial but before primary outcome was recorded (n = 2).
cDelivery 1 to 2 days after entering the trial and no primary outcome recorded (n = 1); delivery more than 2 days after entering the trial but before primary outcome was recorded (n = 9).
dDelivery date not recorded so primary outcome could not be determined (n = 4); delivery more than 2 days after entering the trial but before primary outcome was recorded (n = 2).
eDelivery date not recorded so primary outcome could not be determined (n = 1); delivery more than 2 days after entering the trial but before primary outcome was recorded (n = 8).
