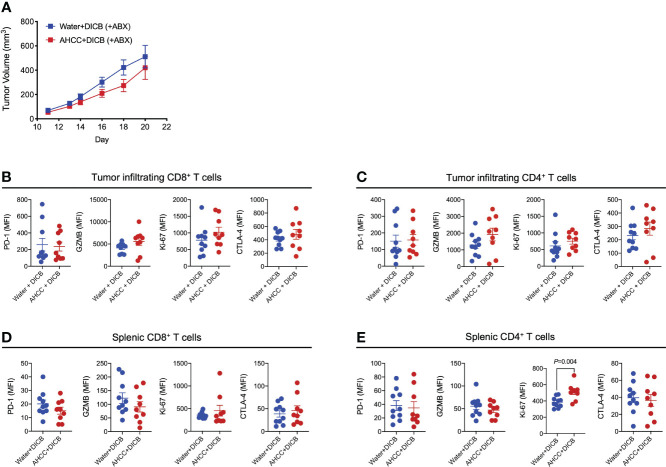
Figure 4.
Administration of antibiotics abrogates the additive anti-tumor effect of AHCC® in MC38 tumor-bearing mice treated with dual PD-1/CTLA-4 blockade. Mice were treated for approximately 3 weeks prior to subcutaneous MC38 tumor inoculation with a combination of 3 antibiotics (ampicillin, streptomycin, and colistin) by adding the drugs to drinking water and continued until sacrifice. As described in Figure 1A, tumor bearing mice were subsequently treated with water or AHCC® in addition to dual PD-1/CTLA-4 blockade i.p. injection (50 µg each, twice at 3-day intervals). (A) Tumor growth was determined by measuring tumor volume (mm3). Flow cytometric analysis of PD-1, granzyme B (GZMB), Ki-67, and CTLA-4 expression (mean fluorescent intensity or MFI) by tumor-infiltrating (B, C) and splenic (D, E) CD8+ and CD4+ T cells. Each dot indicates one mouse (n =9-10/group). Lines and error bars indicate mean ± standard error of mean (SEM), respectively. Data from two independent experiments. P values were determined using the unpaired Student’s t-test.