Figure 7.
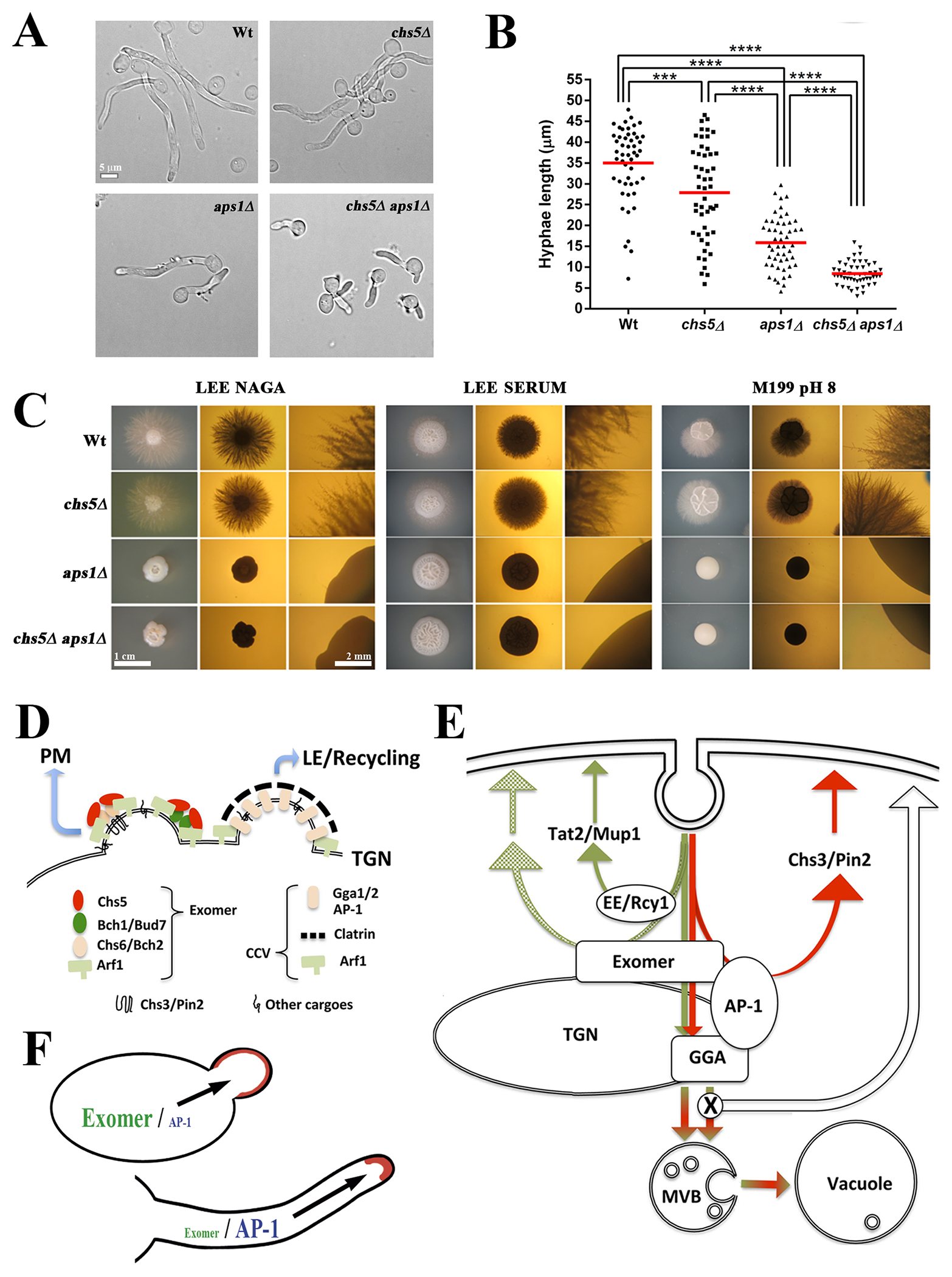
Exomer and clathrin adaptors in protein sorting: implications of exomer and AP-1 relationship in Candida albicans physiology and a model for TGN sorting. (A) C. albicans cells of the indicated strains were induced for filamentation at 37ºC in filamentation media (YEPD, 80 mg/L uridine and 10 % fetal bovine serum). Images were acquired after 2 hours of growth. (B) Quantification of the length of the hyphae in the experiment shown in A. (C) C. albicans filamentation in different solid media. Individual cells were plated onto the indicated filamentation media and incubated for 3–4 days at 37ºC. Images were acquired with a stereomicroscope with upper (left panel) or lower (central and right panels) illumination. Right panels present images with a higher amplification to show the details of filamentation (scales 1cm and 2mm). Note the absence of hyphae in the aps1∆ and aps1∆ chs5∆ mutants under all conditions tested. All tested strains are diploids and homozygous for the indicated genes. (D) Exomer and CCV are assembled at nearby localizations of the TGN and share a requirement for Arf1-GTPase activity. Exomer assembles as different complexes with different properties and facilitates the anterograde delivery of multiple proteins to the PM. CCV vesicles facilitate the late endosomal traffic of several proteins, affecting their recycling. (E) Exomer is required for the transport to the PM of a limited set of proteins that interact with both the exomer and AP-1 complexes (red lines). The anterograde traffic and the recycling of these bona fide exomer cargoes strictly depend on the coordinated action of both exomer and AP-1, a distinctive characteristic of S. cerevisiae cells. By contrast, exomer has a more general role in protein sorting at the TGN region that facilities polarized delivery of multiple proteins to the PM, independent of Rcy1-mediated recycling (green lines). In addition, exomer contributes to the correct assembly of the clathrin adaptor complexes, thereby, facilitating the proper late endosomal traffic of multiple proteins through the vacuole. Disruption of these clathrin adaptor complexes allows the transit of all these proteins to the PM by alternative pathways. PM: plasma membrane, TGN: trans-Golgi network; MVB: multi vesicular body. (F) A diagram showing the differential role of the exomer and AP-1 complexes in the polarized growth of fungi depending on how cells grow as yeasts or as hyphae.
