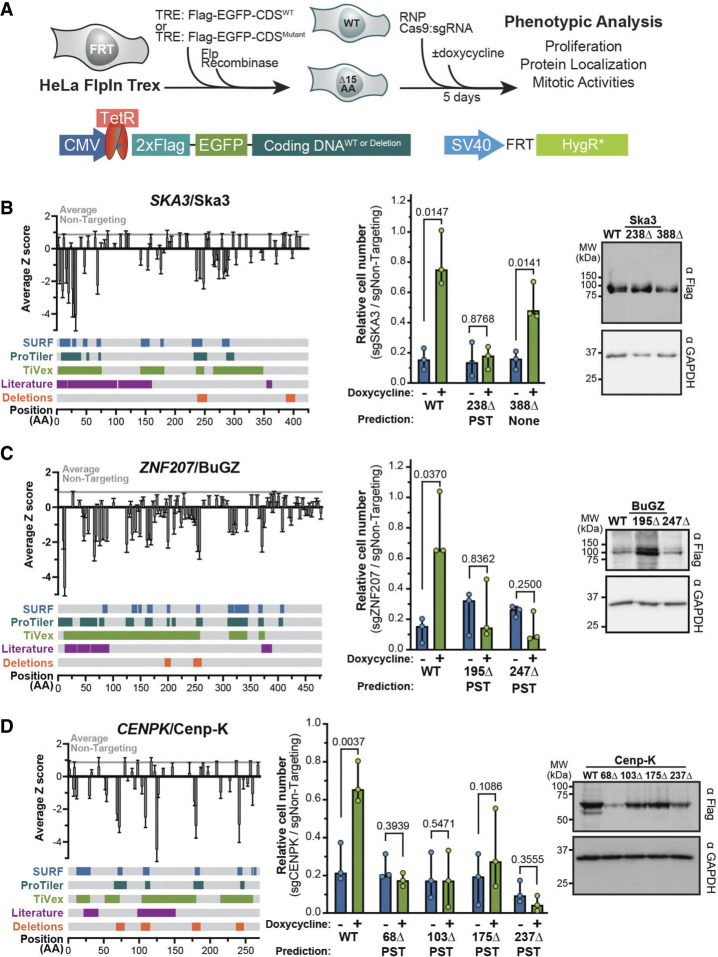
Figure 4.
Functional validation and characterization of 11 high-resolution regions within five genes identified by tiling. (A) Schematic of generating cell lines in which expression of wild-type or mutant proteins is induced by doxycycline and the CRISPR/Cas9-based complementation approach used for functional validation. (B–D) Tiling profile, validation of the proliferation phenotype, and assay of protein stability for SKA3/Ska3 (B), ZNF207/BuGZ (C), and CENPK/Cenp-K (D). Tiling profiles are the same as in Figure 3 while also showing regions that were deleted. Cell proliferation was assayed as the cell number after knockout of endogenous protein relative to a nontargeting control in the presence (green) or absence (blue) of doxycycline. Cell numbers were normalized to the same cell line electroporated with a nontargeting control. The analysis methods predicting a region to be essential shown as P (ProTiler), S (CRISPR–SURF), and T (TiVex). Each dot is a biological replicate, with bars showing median values and 95% confidence intervals. Paired t-tests were used to determine P-values. Steady-state protein levels of wild-type and mutant proteins were assayed by immunoblot in the presence of endogenous protein, using GAPDH as a loading control and exposed for a shorter interval. For more examples, see Supplemental Figure S4.