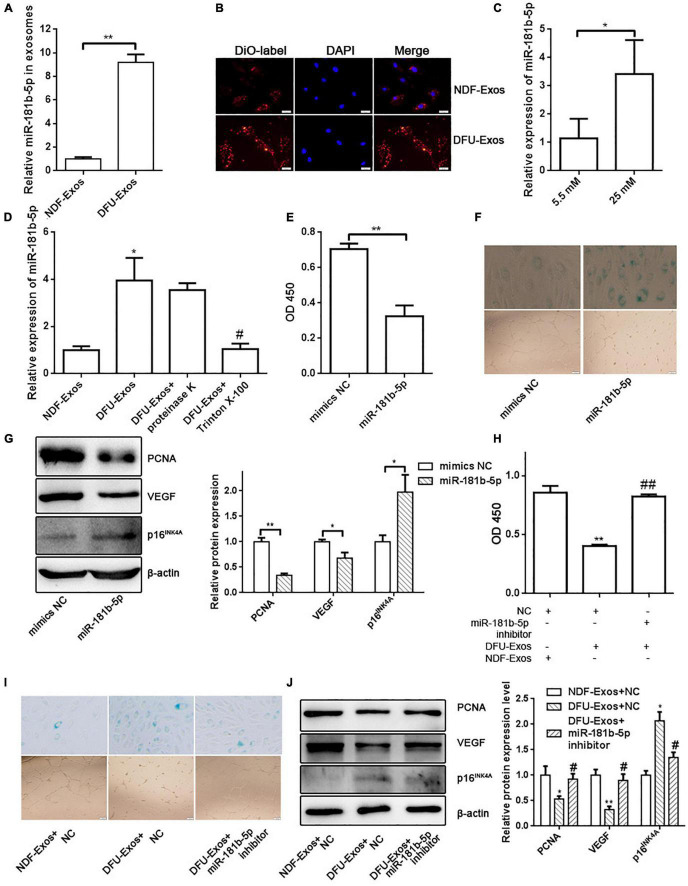
FIGURE 2.
Exosomal miR-181b-5p from DFU-Exos promoted cell senescence and inhibited tube formation in HUVECs. (A) miR-181b-5p expression in NDF-Exos and DFU-Exos detected by qRT-PCR. **P < 0.01 DFU-Exos vs. NDF-Exos. (B) DiO-labeled showing the uptake of exosomes by HUVECs. (C) miR-181b-5p level in exosomes isolated from HUVECs cells grown in culture medium containing 5.5 mM or 25 mM glucose. *P < 0.05 5.5 mM vs. 25 mM. (D) miR-181b-5p level in HUVECs was detected by qRT-PCR. *P < 0.05 vs. NDF-Exos, #P < 0.05 vs. DFU-Exos. CCK-8 assay (E), β-gal staining and tube formation (F) were used to detect the effects of miR-181b-5p on cell viability, cell senescence and tube formation. **P < 0.01 miR-181b-5p vs. mimics NC. (G) Western blotting showing the expression of PCNA, VEGF, and p16INK4A in HUVECs overexpressing miR-181b-5p. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 miR-181b-5p vs. mimics NC. CCK-8 assay (H), β-gal staining and tube formation (I) showing cell viability, senescence and tube formation in rescue experiment. **P < 0.01 vs. NC + NDF-Exos, ##P < 0.01 vs. NC + DFU-Exos. (J) Western blotting showing the expression of PCNA, VEGF, and p16INK4A in HUVECs. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. NDF-Exos + NC, #P < 0.05 vs. DFU-Exos + NC.