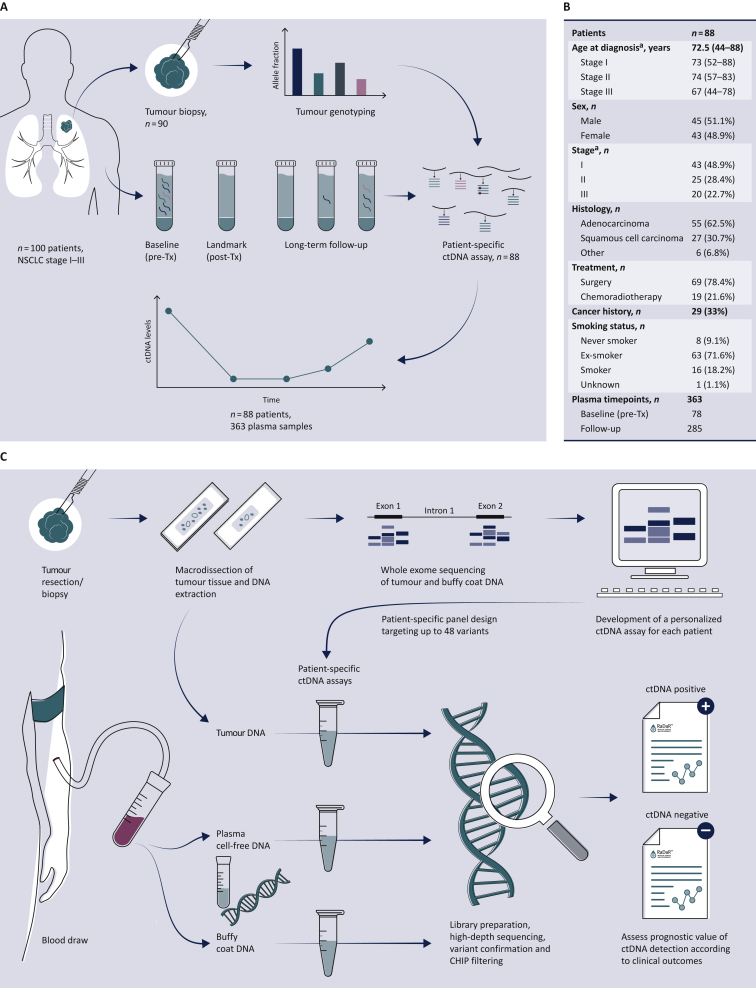
Figure 1.
Study overview.
(A) Study design: 100 patients with NSCLC stage I-III were recruited to the LUCID study. For 90 patients, tumour specimens were available and were analyzed by whole exome sequencing (WES), to identify somatic single nucleotide variants for design of patient-specific assays. Assays were successfully developed (panel B) for 88 patients. A total of 363 plasma samples collected from these patients at multiple timepoints before and after treatment were analyzed using those personalized assays to detect ctDNA and estimate its fractional concentration. The prognostic value of ctDNA detection was assessed by comparing ctDNA data with clinical outcomes to evaluate the relapse-free survival and overall survival for patient subgroups. A CONSORT flow diagram is provided in Supplementary Figure S1, available at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2022.02.007. (B) Patient demographics of the 88 patients enrolled in the LUCID study who had available tumour tissue for sequencing and a patient-specific ctDNA assay successfully designed.
ca., carcinoma; ctDNA, circulating tumour DNA; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; Tx, treatment.
aCancer stage was defined at the time of diagnosis according to diagnostic pathways,30 and was updated after surgery based on pathological analysis of the tumour specimen for patients who underwent surgery. (C) Overview of the workflow involved in the development of the RaDaR™ sequencing assays used in this study. Personalized sequencing assays were designed based on WES data from tumour and buffy coat samples, targeting 48 somatic variants for each assay. These were used to amplify regions in plasma cell-free DNA, tumour DNA and buffy coat DNA using multiplex PCR and high-depth next generation sequencing. Data from tumour DNA and buffy coat samples were used to confirm the detection of somatic variants and to exclude variants which may derive from clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP). Plasma samples were classified as ctDNA positive (detected) or ctDNA negative (not detected) based on the RaDaR™ assay sequencing data and analytical pipeline, and the estimated variant allele fraction (eVAF) was calculated.