Figure 6.
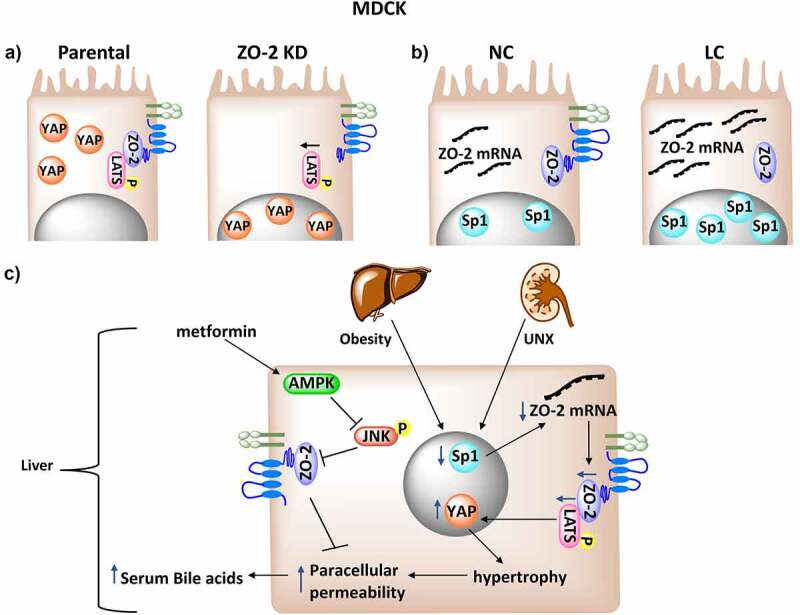
ZO-2 silencing diminishes LATS activation, favoring the nuclear concentration of YAP and the development of hypertrophy. A) ZO-2 functions as a scaffold at the TJ that facilitates LATS phosphorylation and inhibits the nuclear concentration of YAP. B) In confluent cultures of MDCK cells incubated in medium with low calcium (LC), TJs cannot be established, but the cells accumulate SP1 transcription factor and ZO-2 mRNA. C) In hypertrophic kidney and in the liver with steatosis, ZO-2 silencing is generated by a decrease in ZO-2 transcription probably associated to a diminished nuclear content of Sp1 transcription factor. ZO-2 interacts with LATS, and the reduced expression of ZO-2 blocks LATS phosphorylation and activation facilitating the nuclear concentration of YAP. In the steatotic liver this condition triggers an increase in paracellular permeability of hepatocytes and the presence of bile acids in serum. Metformin, via AMPKα1 activation inhibits JNK signaling that promotes TJ barrier dysfunction.
