Figure 7.
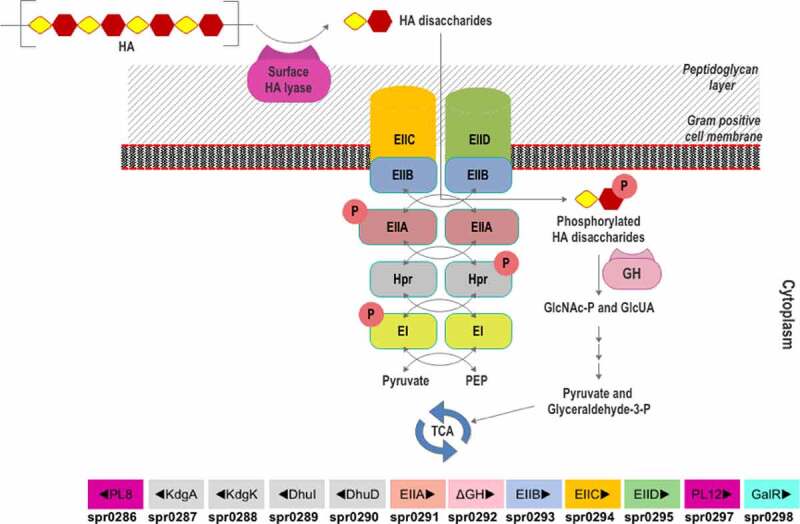
Scheme of HA utilization by Streptococcus pneumoniae R6. Extracellular HA is acquired and fragmented by a surface hyaluronidase to unsaturated HA disaccharides. Internalization of HAΔdi occurs via the phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cascade of PTS subunits (EI and EIIA-EIID), HPr protein, pyruvate, and phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). The GlcNAc-phosphorylated HAΔdi is decomposed into monosaccharides (GlcA and GlcNAc-P) in the cytoplasm by an unsaturated glycoside hydrolase (GH). The monosaccharides are funneled through various enzymatic reactions to the energy production pathway. The HA-gpPUL with the gene numbers of the bacteria is shown at the bottom. PL8: hyaluronidase; KdgA: 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate aldolase: KdgK: 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate kinase; DhuI: 4-deoxy-L-threo-5-hexosulose-uronate ketol-isomerase; DhuD: 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-gluconate dehydrogenase; EIIA-EIID: Enzyme complex II subunit A to D of PTS system; PL12: putative heparinase; GalR: galactose operon repressor type transcription regulator; EI: Enzyme complex I of PTS system; Hpr: Hpr protein of PTS system.
