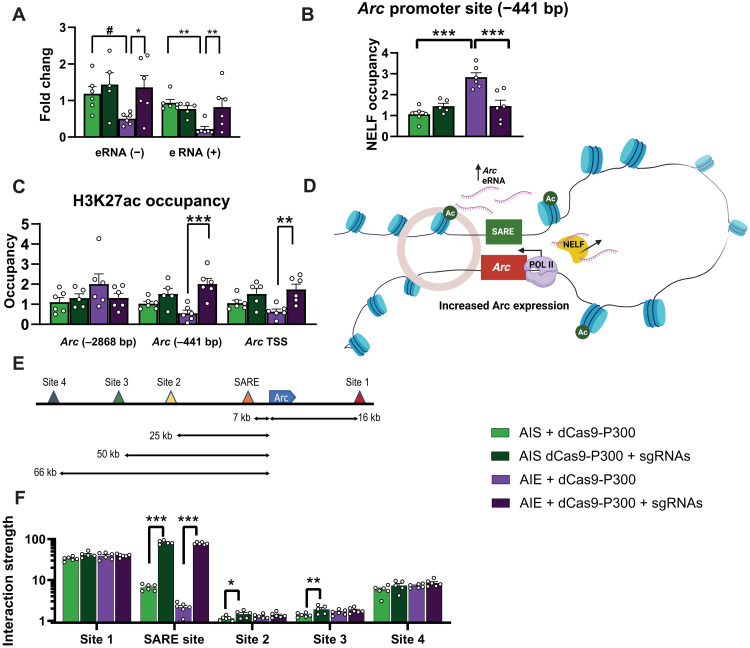
Fig. 2. dCas9-P300 plus sgRNAs reverses deficits in eRNA expression and increases enhancer and promoter interactions.
(A) dCas9-P300 plus sgRNAs reverses AIE-induced decreases in Arc eRNA (+) expression (adolescent exposure × lentivirus interaction F1,19 = 6.96, P = 0.016) and Arc eRNA (−) expression (lentivirus, F1,19 = 5.25, P = 0.034). (B) dCas9-P300 plus sgRNAs releases NELF from the Arc promoter (−441 bp) in the amygdala of AIE adult rats (adolescent exposure: F1,19 = 17.58, P < 0.001; adolescent exposure × lentivirus interaction: F1,19 = 17.55, P < 0.001). (C) dCas9-P300 plus sgRNAs reverses AIE-induced decrease in H3K27ac occupancy at Arc promoter (−441 bp) (adolescent exposure × lentivirus interaction: F1,19 = 5.45, P = 0.031) and Arc TSS (lentivirus: F1,19 = 14.21, P = 0.001) without any effects at distal to the TSS (−2868 bp). (D) Hypothetical model of chromatin looping most likely produced by dCas9-P300 in adult amygdala after AIE leading to increase in H3K27ac levels at Arc promoter (−441 bp and TSS) and release of NELF to increase Arc expression. (E) Arc gene showing the locations of sites including SARE that were selected to evaluate the interaction with promoter (blue color). (F) 3C assay shows that dCas9-P300 plus sgRNAs reverses lower interactive strength between Arc promoter and SARE in the amygdala of AIE adult rats (lentivirus: F1,19 = 1540.74, P < 0.001) and minimal effect of virus in AIS group at sites 2 and 3 but no change at sites 1 and 4 of the gene. Two-way ANOVAs were followed by Tukey’s post hoc test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; #P = 0.056). Bar graphs show means ± SEM (n = 5 to 6 rats in each group), and individual values are shown with circle dots on bar graphs.