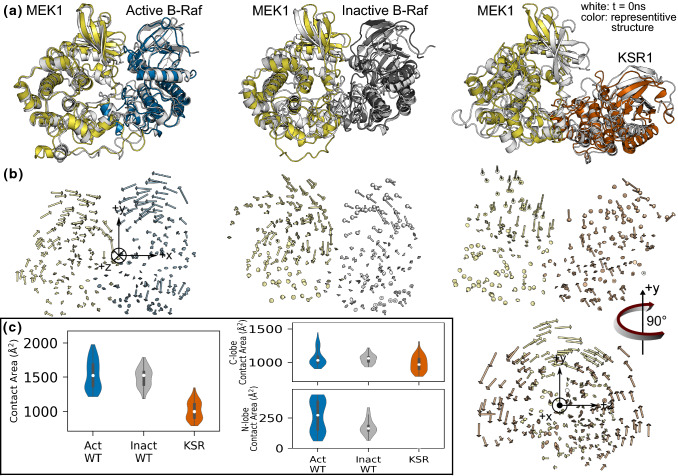
Fig. 2.
a Snapshots comparing the initial structure with the most representative structure for the B-Raf/MEK1 and KSR1/MEK1 heterodimers. The N-lobes in B-Raf and MEK1 move towards each other while the N-lobes of KSR1 and MEK1 move apart. Cartoon drawings of the initial configuration (white) and a representative snapshot of the active wild-type B-Raf/MEK1 (blue/yellow), inactive wild-type B-Raf/MEK1 (gray/yellow) and KSR1/MEK1 (orange/yellow) systems. b First normal mode of every other residue for the same systems as above. c Total contact area, C-lobe to C-lobe contact area, and N-lobe to N-lobe contact area for active wild-type B-Raf/MEK1 (Act WT), inactive wild-type B-Raf/MEK1 (Inact WT) and KSR1/MEK1 (KSR) systems