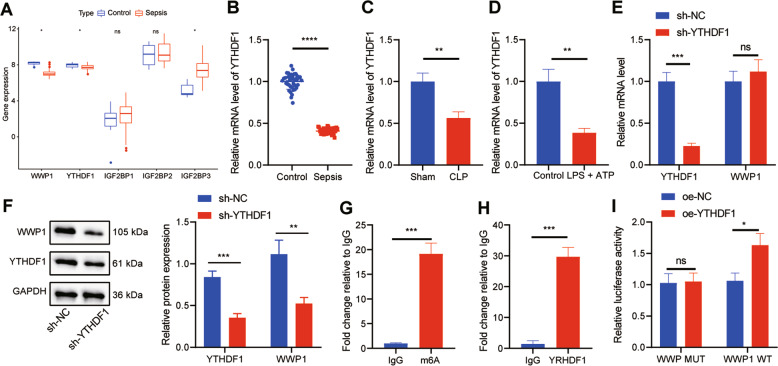
Fig. 3. YTHDF1 facilitates WWP1 expression in LPS + ATP-treated RAW264.7 cells.
A The expression of WWP1 and four m6A readers in sepsis-related microarray GSE00159 (measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and paired samples t test was applied for comparison between the control group and the sepsis group). B RT-qPCR to detect the expression of YTHDF1 in PBMCs of sepsis samples (n = 40) and healthy controls (n = 40). C The expression of YTHDF1 in PBMCs of mice with different treatment detected by RT-qPCR. D The expression of YTHDF1 determined by RT-qPCR. E The expression of YTHDF1 and WWP1 in cells with different treatment assessed by RT-qPCR. F Western blot assay to measure the protein expression of YTHDF1 and WWP1 in cells with different treatment. G The m6A modification status of WWP1 mRNA evaluated by meRIP. H, RIP-RT-qPCR to assess the binding of WWP1 mRNA to YTHDF1 protein. I Dual luciferase gene reporter assay to evaluate the binding of WWP1 and YTHDF1. There were 10 mice in each group. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. ****p < 0.0001. ‘ns’ indicates no significant difference. Cell experiments were repeated three times.