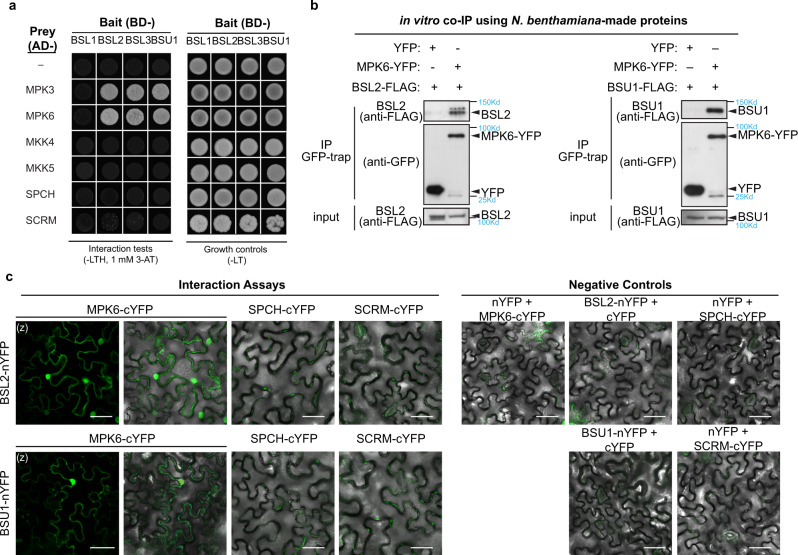
Fig. 5. BSL2/BSL3/BSU1 interact with MPK6.
a Results of yeast two-hybrid assays show BSL2/BSL3/BSU1 proteins directly interact with MPK3/6. Bait, “BD-” indicates Gal4 DNA-binding domain; Prey, “AD-” indicates Gal4 activation domain. “Growth controls”, assays performed using rich media (-Leu-Trp); “Interaction tests”, assays performed using synthetic dropout medium (-Leu-Trp-His; 1 mM 3-AT added to suppress bait auto-activation). b Co-IP assays using purified fusion proteins produced by N. benthamiana leaves show physical association of BSL2-FLAG (left) or BSU1-FLAG (right) with MPK6-YFP. YFP (left lane, - control) or MPK6-YFP (right lane) was used as bait to bind to the GFP-Trap agarose. Immunoprecipitated proteins were detected by anti-FLAG. Data represent results of three biological repeats. c Results of bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays in N. benthamiana leaf epidermal cells show BSL2 and BSU1 interact with MPK6 in plant cells. YFP signals (green) indicate protein-protein interactions. No interactions were detected between BSL2/BSU1 and the transcription factors SPCH/SCRM. nYFP, N-terminal YFP; cYFP, C-terminal YFP. Data represent results of three independent experiments. Scale, 50 μm. (z), z-staked confocal images.