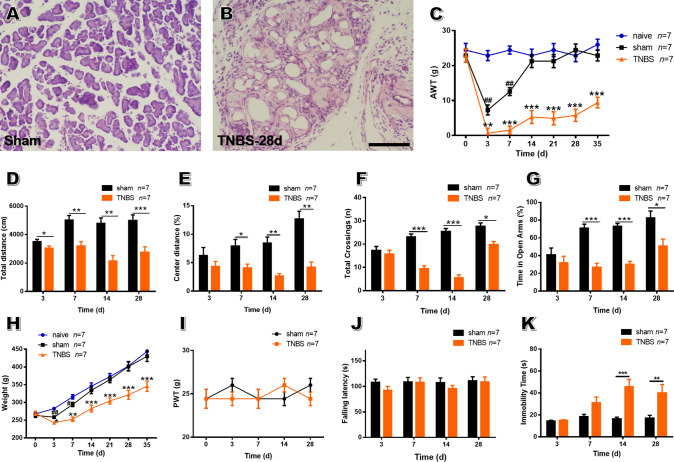
Fig. 1.
Chronic pancreatitis induced by TNBS elicits abdominal hyperalgesia and anxiety-like behaviors in rats. A, B Representative H&E-stained histological sections of the pancreas on POD 28 in sham and TNBS-treated rats (scale bar, 100 μm). C TNBS-treated rats show a decreased abdomen withdrawal threshold during the course of CP compared to sham rats, while sham rats exhibit transient abdomen mechanical hypersensitivity that returns to baseline on POD 14 (n = 7 rats per group; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, TNBS vs sham; ##P < 0.01, sham vs naïve, one-way repeated ANOVA). D, E CP rats travel shorter distances (D) from POD 3 to 28 and travel less distance in the center area (E) from POD 7 to 28 in the open field test than sham rats. F, G CP rats exhibit fewer crossings (F) and less time in the open arms (G) in the high elevated maze test than sham rats from POD 3 to 28 (n = 7 per group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, TNBS vs sham, unpaired t-test). H CP rats lose body weight during the course of CP compared to sham rats, while sham rats show a transient weight loss from POD 3 to 7 which returns to baseline after POD 14 (n = 7 per group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, TNBS vs sham; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, sham vs naïve, one-way repeated ANOVA). I CP rats exhibit no significant change in hindpaw withdrawal threshold compared with the sham group (P > 0.05, n = 7 per group, one-way repeated ANOVA). J, K No change in falling latency between CP and sham rats in the rotarod test (J), while CP rats exhibited a prolonged immobility time in the forced swimming test from POD 14 to 28 (K) (n = 7 per group; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, TNBS vs sham, unpaired t-test). AWT, abdomen withdrawal threshold; PWT, paw withdrawal threshold; TNBS, trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid.