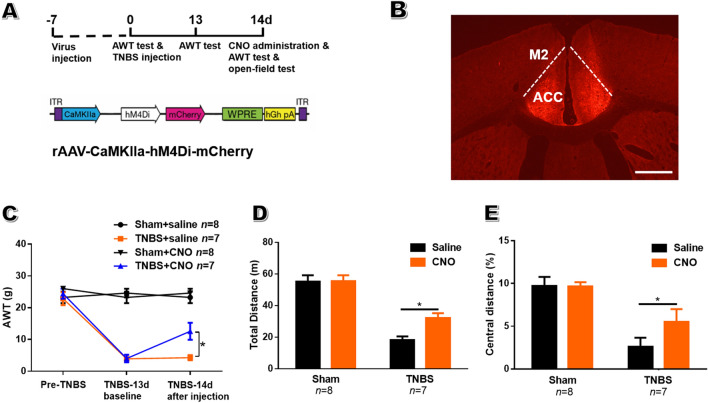
Fig. 8.
Chemogenetic inhibition of bilateral ACC pyramidal neurons alleviates abdominal hyperalgesia and anxiety-like behavior in CP rats. A Upper panel, schematic of the behavioral experiment; lower panel, rAAV-CaMKIIa-hM4Di-mCherry construct. B Representative coronal section showing the injection sites in the ACC (scale bar, 1 mm). C Inhibiting bilateral pyramidal neurons in the ACC via intraperitoneal CNO significantly increases the AWT in CP rats but not sham rats. D, E Inhibiting ACC neurons significantly reduces the total distance (D) and the distance traveled in the center (E) of the open field in CP rats but not sham rats (n = 8 for sham and 7 for CP rats; *P < 0.05, TNBS vs sham, unpaired t-test). ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; M2, secondary motor cortex.