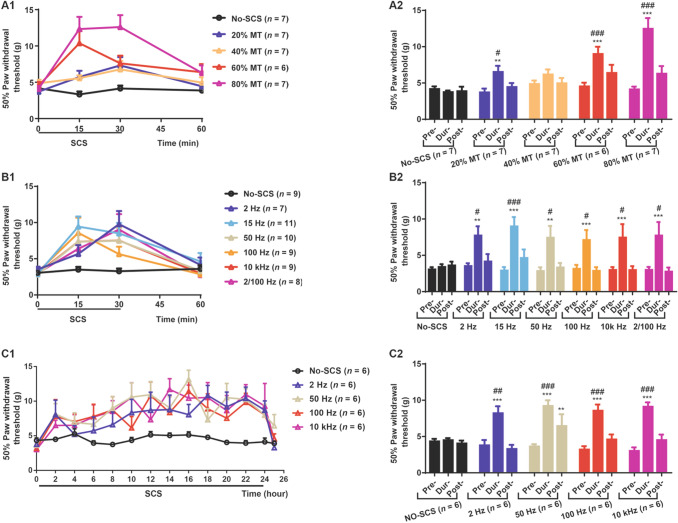
Fig. 4.
The analgesic effect of SCS at different intensities and frequencies in short-term SCS and the effect of continuous prolonged SCS at 4 frequencies. A1, A2 Time course of the analgesic effect at different MTs of SCS at 50 Hz. There is an intensity-dependent and reversible elevation in the 50% PWT in rats with moderate mechanical hypersensitivity (also see Table S1). It appears that SCS at 60% MT or above is required to have a reliable analgesic effect. B1, B2 Time course of the analgesic effect of SCS at different frequencies at 80% MT. All frequencies (2, 15, 50, 100 Hz, 10 kHz, and 2/100 Hz alternating frequencies) of SCS showed similar degrees of analgesic effects in rats with moderate mechanical hypersensitivity. For short-term SCS, Pre-SCS represents the 50% PWT at 0 min in A1 and B1; Dur-SCS, mean 50% PWT at 15 and 30 min in B1; Post-SCS, 50% PWT at 60 min in A1 and B1. C1, C2 Time course for changes in 50% PWT during and after prolonged SCS in 80% MT at four frequencies. Prolonged SCS up to 24 h at 2, 50, 100 Hz, and 10 kHz had a similar persistent analgesic effect. The analgesic effect disappeared 1 h after termination of the SCS except in the 50 Hz group. Pre-SCS, 50% PWT at time 0 in C1; Dur-SCS, mean 50% PWT every 2 h from 2 to 24 h in C1; Post-SCS, 50% PWT at 25 h in C1. Repeated ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparisons test; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs Pre-SCS; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs Dur-SCS in the No-SCS group.