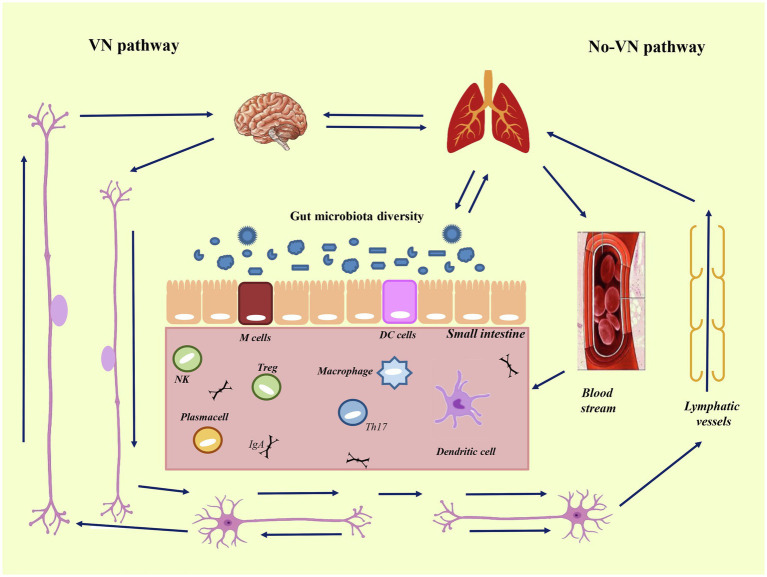
Figure 5.
Intestine-lung-brain axis. Bidirectional axis between intestine, lung, and brain. Axis mean the pathways and cross-talks that occur between distal body sites, such as intestine, brain, and lung. The cross-talk takes place through blood stream and via lymphatic vessels (via non-VN-pathway), and via autonomic nervous system (via the vague-nervous). To the left is reported the vague-nervous pathway (VN-pathway), and to the right the non-VN-pathway, that is composed by blood stream and lymphatic vessels. The communication routes involve the autonomic nervous system (enteric nervous system and vagus nerve) and the immune system linked to the neuroendocrine system. These connected systems can affect each other in particular when the immune system, underlying the gut epithelium, became activated. Modified from Santos et al. (2019).