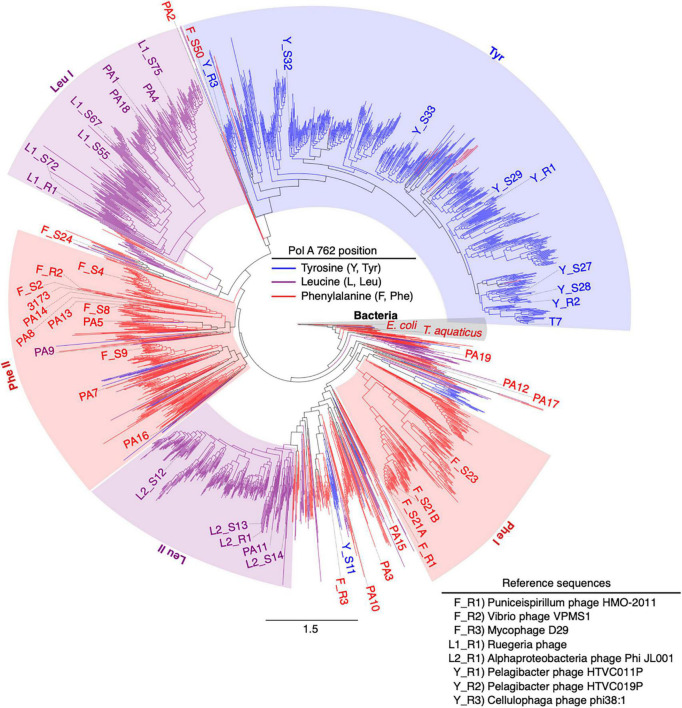
FIGURE 1.
Synthesized family A DNA polymerase sequences span phylogenetic diversity. Approximate maximum likelihood tree of 2,130 PolA amino acid sequences trimmed to the region of interest (DNA_pol_A Superfamily, acc. cl02626), the polymerase domain. Branch coloring indicates residue identity at the 762 position within the protein sequence. Synthesized reference and virome sequences are labeled by 762 residue monophyletic clades [leucine, Leu I or Leu II; tyrosine, Tyr; (Nasko et al., 2018)] with two additional paraphyletic groups identified in this analysis (phenylalanine, Phe I or Phe II). Phe I and Phe II. Bacterial reference sequences clustered toward the root of the tree are shaded in gray. All synthesized sequences are labeled by source (reference, R; virome, S; or IMG/M database, PA). PolA with previously published biochemical characterization are labeled separately (T7, E. coli, 3173, and T. aquaticus). Scale bar represents the number of amino acid substitutions per site.