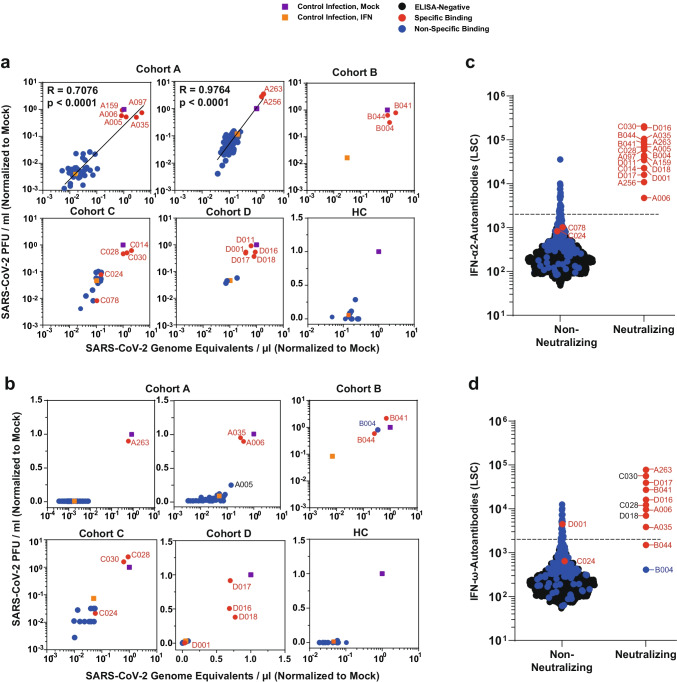
Fig. 2.
IFN-AABs neutralize exogenous IFN in a virus infection-based assay. a, b Selected sera were analyzed for IFN neutralization activity in a SARS-CoV-2 infection-based assay. The ability of individual sera to neutralize exogenous IFN-α2 (a) and IFN-ω (b) is shown by the rescue of susceptibility to infection as judged by quantification of viral RNA (x-axis) and infectivity (y-axis) in the supernatant. The infection condition in the absence of serum and IFN is set to 1. c, d The LSC value for individual sera, grouped into non-neutralizing and neutralizing sera, for the four COVID-19 cohorts. Dots indicate sera containing AABs scoring specific (red) or unspecific (blue) for IFN-α2 and IFN-ω binding in the competition assay (see b), respectively. Black dots indicate samples that scored below the threshold of the ELISA. Black dotted lines indicate the 97.5th percentile of the ECLIA assay LSC in sera from the healthy health care workers (HC) cohort (see Fig. 1). Neutralization ability of IFN-α and IFN-ω can be predicted at 100% for sera displaying LSCs above the respective red dotted lines (IFN-α: 35,639; IFN-ω: 12,603)