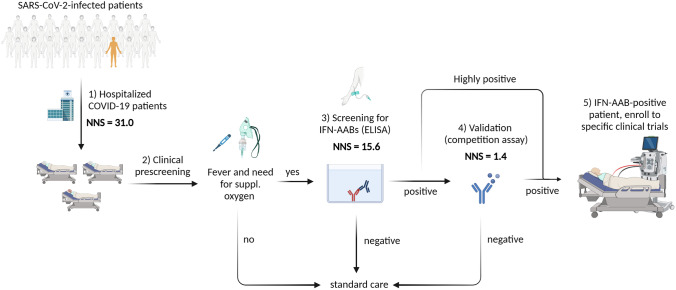
Fig. 7.
Proposed diagnostic algorithm for rapid identification of neutralizing IFN-AAB-positive patients. The number needed to screen (NNS) is based on results from the cross-sectional cohort (CSC). ELISA for IFN-AAB detection was considered to be positive if it exceeded the 97.5th percentile of the healthy control cohort. (1) NNS of all hospitalized COVID-19 patients without preselection was 31.0 (403 patients in total, 13 patients with neutralizing IFN-AABs). (2) Prescreening of patients using the clinical criteria of fever at admission and need for supplemental oxygen within the first 72 h after hospitalization diminished the NNS in the IFN-AAB ELISA (3) by half, to 15.6 (172/11). For patients identified as positive in the screening ELISA, the NNS in the competition assay to confirm the presence of IFN-specific AABs is reduced to 1.4 (15/11) (4). For patients with high-titer IFN-AABs (light signal count > 35.639), the competition assay can be omitted. Patients highly positive in the IFN-AAB ELISA and those with specific results in the competition assay may be included in clinical studies that aim testing specific therapies, including therapeutic plasma exchange (5). Figure created with BioRender.com