Figure 6.
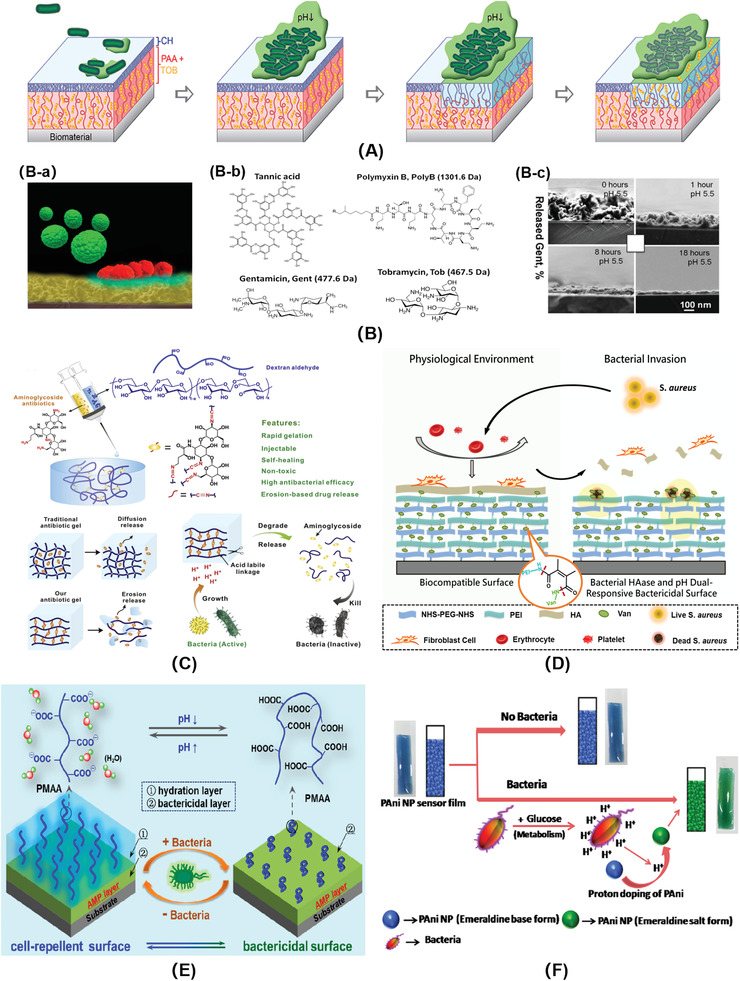
A) A pH‐responsive, drug release polymer bilayer system for the prevention of bacterial infection on biomaterials. Reproduced with permission.[ 137 ] Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society. B‐a) Schematic diagram of bacterial infection microenvironment. B‐b) Chemical structures of polyelectrolyte multilayers components. B‐c) Cross‐sectional SEM images of a (TA/Gent)300 film at different release times. Reproduced with permission.[ 138 ] Copyright 2014, American Chemical Society. C) The smart aminoglycoside hydrogels. The antibiotics served as linkers to form hydrogels with oxidized polysaccharides via an acid‐labile Schiff base linkage. Reproduced with permission.[ 139 ] Copyright 2017, Elsevier. D) Schematic diagram of the bacterial responsive bactericidal and biocompatible surface.[ 143 ] Copyright 2018, Royal Society of Chemistry. E) Nonleaching bacterial acid‐responsive antibacterial surface. Reproduced with permission.[ 144 ] Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society. F) Schematic representation of the PAni‐Pec NPs based colorimetric sensor to monitor bacterial growth. Reproduced with permission.[ 145 ] Copyright 2015, Elsevier.
