Figure 5.
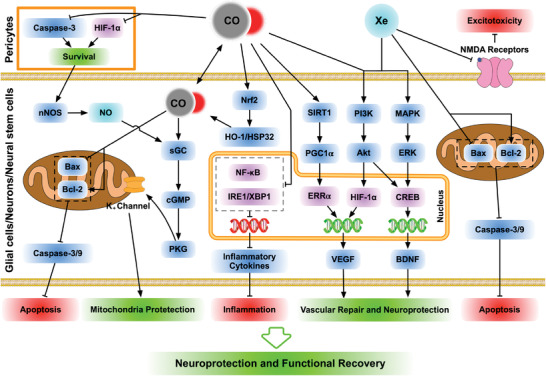
Schematic diagrams of diverging and converging mechanisms underlying the neural protective and recovery effects of carbon monoxide (CO) and xenon (Xe). Left panel: CO impedes IRE1 and NF‐κB via activating Nrf2/HO‐1/HSP in neural cells including neural stem cells (↓inflammatory mediators), and suppresses HIF‐1α and caspases in pericytes (↓cell death). Moreover, CO exerts therapeutic effects through igniting NOS/sGC/PKG to regulate Bax/Bcl2/caspases to augment cell survival, and activating SIRT1/PI3K/MAPK to upregulate VEGF and BDNF. Right panel: Xe protects and repairs neural tissue by antagonizing NMDA receptors to mitigate excitotoxicity, and stimulating PI3K/MAPK, which partly overlaps with the mechanisms of CO. Detailed signaling pathways and target cells are presented in the text and definitions of abbreviations/acronyms in Sections S3 and S4: Supporting Information.
