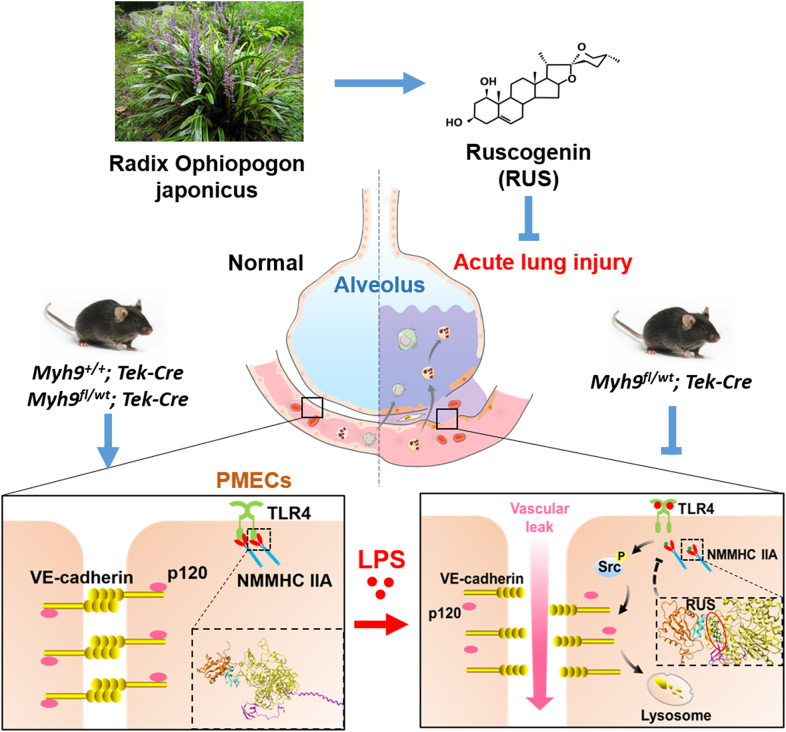
Figure 10.
The graphic illustration of the mechanism of RUS ameliorating LPS-induced pulmonary endothelial barrier dysfunction. NMMHC IIA binds to TLR4 through its N-terminal and head domains as an inactive complex under physiological conditions. Upon LPS binding to TLR4, NMMHC IIA is dissociated from TLR4, initiating downstream signaling and leading to endothelial barrier dysfunction by disruption of VE-cadherin junctions. RUS effectively prevents LPS-induced pulmonary endothelial barrier disruption by targeting NMMHC IIA and modulating NMMHC IIA‒TLR4 interactions. PMECs, pulmonary vascular endothelial cells; p120, p120-catenin.