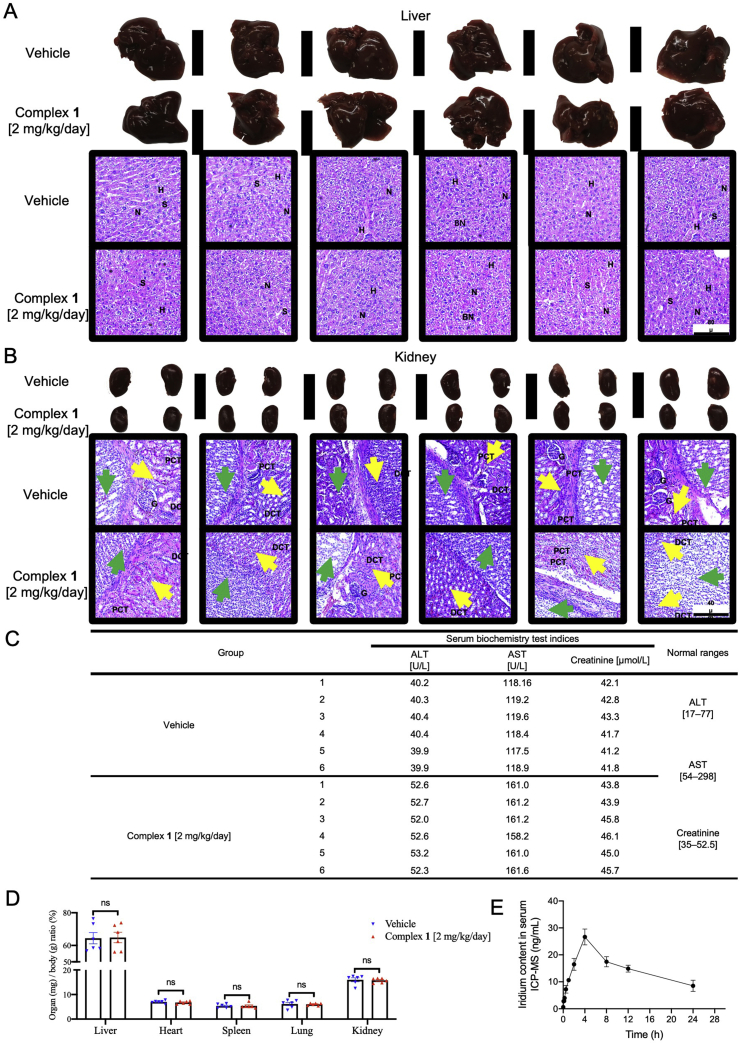
Figure 8.
The toxicity and pharmacokinetic profiles of complex 1. Twelve female mice were randomly divided into two groups and were treated with 1 (2 mg/kg/day) for 18 days. Histological examination of liver and kidney injury. (A) Liver specimens and corresponding H&E staining images indicated the hepatic architecture with nucleus (N), hepatocytes (H), and sinusoids (S) in both vehicle and 1 (2 mg/kg/day) treated group. None of significant hepatic centrilobular mononuclear cell infiltration, fatty changes, nor hepatic cell necrosis were observed, except for sporadic binucleated hepatocytes (BN) in both groups. Scale bar = 80 μm (×10). (B) Kidney specimens and corresponding H&E staining images showed the histological structure with glomerulus (G), proximal convoluted tubules (PCT), and distal convoluted tubules (DCT) in both vehicle and 1 (2 mg/kg/day) treated group. Yellow arrows indicate the renal medulla; green arrows indicate renal pelvis. None pyknotic cells, distal tubular necrosis, sloughing of tubular epithelial cells, nor proximal hemorrhage in interstitial tissue were identified. Scale bar = 40 μm (×20). (C) Serum alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), creatinine levels, and corresponding normal ranges of vehicle and 1 (2 mg/kg/day) treated mice. (D) Normalized organ weights as percentages of body weight. Mice given vehicle and 1 (2 mg/kg/day) were sacrificed at Day 18, the normalized ratio were calculated: organs weight divided by body weight as mg/g, not significant (ns). (E) Pharmacokinetic profile of 1 at different time points. BALB/c mice were intraperitoneally injected with 1 (2 mg/kg/day). The concentrations of 1 in the serum were measured at 0, 0.08, 0.17, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24 h. All data were mean ± SEM from 6 mice per treatment group. Significance was determined using one-way ANOVA analysis.