Figure 1: Distinct prevalence and features of aneuploidy in WGD− and WGD+ tumors.
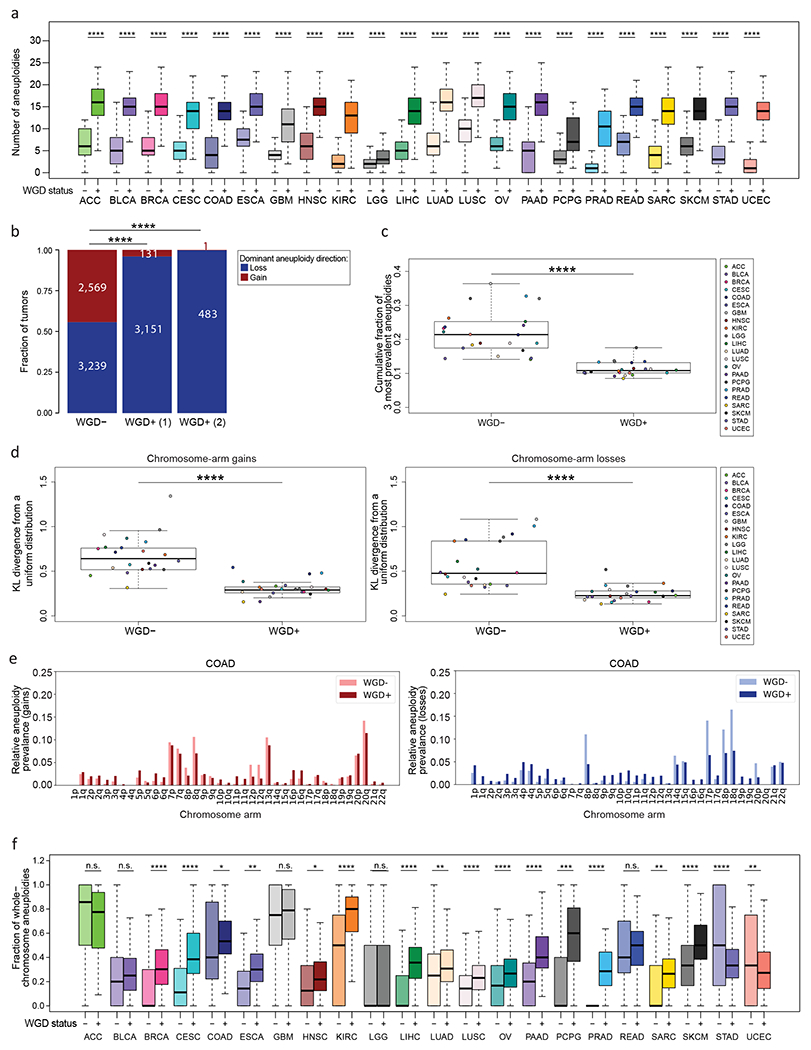
(a) Comparison of the number of aneuploidies between WGD− and WGD+ tumors across 22 tumor types. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; ****, p<0.0001; adjusted two-tailed Student’s t-test. (b) Comparison of the dominant whole-chromosome aneuploidy direction (i.e., the fraction of WGD−, WGD+ (1) and WGD+ (2) tumors with ploidy below or above the basal ploidies of 2n, 4n or 8n, respectively) between WGD− and WGD+ tumors, across all cancer types combined. p=2<2-16; two-tailed Fisher’s Exact test. (c) Comparison of the cumulative fraction of the top three aneuploidies (out of all aneuploidies) between the WGD− and WGD+ tumors, across the 22 tumor types. ****, p=3e-9; two-tailed Student’s t-test. (d) Comparison of the deviation of chromosome-arm gains (left) and losses (right) from a uniform distribution, between WGD− and WGD+ tumors, across the 22 tumor types. ****, p=8e-08 and p=4e-07, for gains and losses, respectively; two-tailed paired Student’s paired t-test. (e) The relative prevalence of chromosome-arm gains (left) and losses (right) in WGD− and WGD+ colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) tumors. (f) Comparison of the fraction of whole-chromosome aneuploidies (out of all whole-chromosome and arm-level aneuploidies) between WGD− and WGD+ tumors within 22 tumor types. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; ****, p<0.0001; adjusted two-tailed Student’s t-test. ACC, adrenocortical carcinoma; BLCA, bladder urothelial carcinoma; BRCA, breast invasive carcinoma; CESC, Cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma; COAD, colon adenocarcinoma; ESCA, esophageal carcinoma; GBM, glioblastoma multiforme; HNSC, Head and Neck squamous cell carcinoma; KIRC, Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; LGG, Brain lower grad glioma; LIHC, Liver hepatocellular carcinoma; LUAD, Lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC, Lung squamous cell carcinoma; OV, Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma; PAAD, Pancreatic adenocarcinoma; PCPG, Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma; PRAD, Prostate adenocarcinoma; READ, Rectum adenocarcinoma; SARC, sarcoma; SKCM, Skin Cutaneous Melanoma; STAD, Stomach adenocarcinoma; UCEC., Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma
