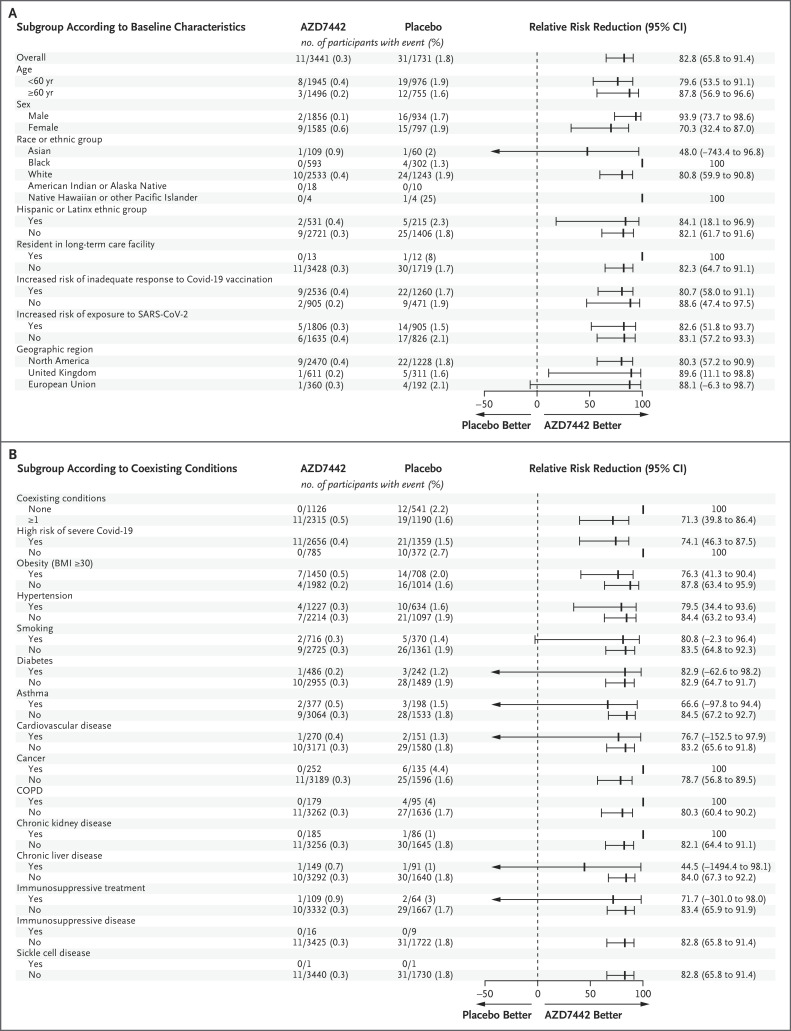
Figure 1. Relative Risk Reduction in the Incidence of the First SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR–Positive Symptomatic Illness with AZD7442 as Compared with Placebo, at a Median 6-Month Follow-up.
Estimates are based on Poisson regression with robust variance with the use of a full model or reduced model. An estimated relative risk reduction greater than 0 favored AZD7442. Panel A shows the relative risk reduction according to the baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of the participants. The relative risk reduction with AZD7442 could not be estimated for participants of American Indian or Alaskan Native heritage or those with immunosuppressive disease or sickle cell disease, because there were no instances of SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR–positive symptomatic illness in participants in those subgroups. Panel B shows the relative risk reduction according to the participants’ coexisting conditions. The body-mass index (BMI) is the weight in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters. Immunosuppressive treatment is medication that suppresses the immune response, and immunosuppressive disease is a medical condition that could suppress the immune response, regardless of treatment. CI denotes confidence interval, COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Covid-19 coronavirus disease 2019, NE not estimable, RT-PCR reverse-transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction, and SARS-CoV-2 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.