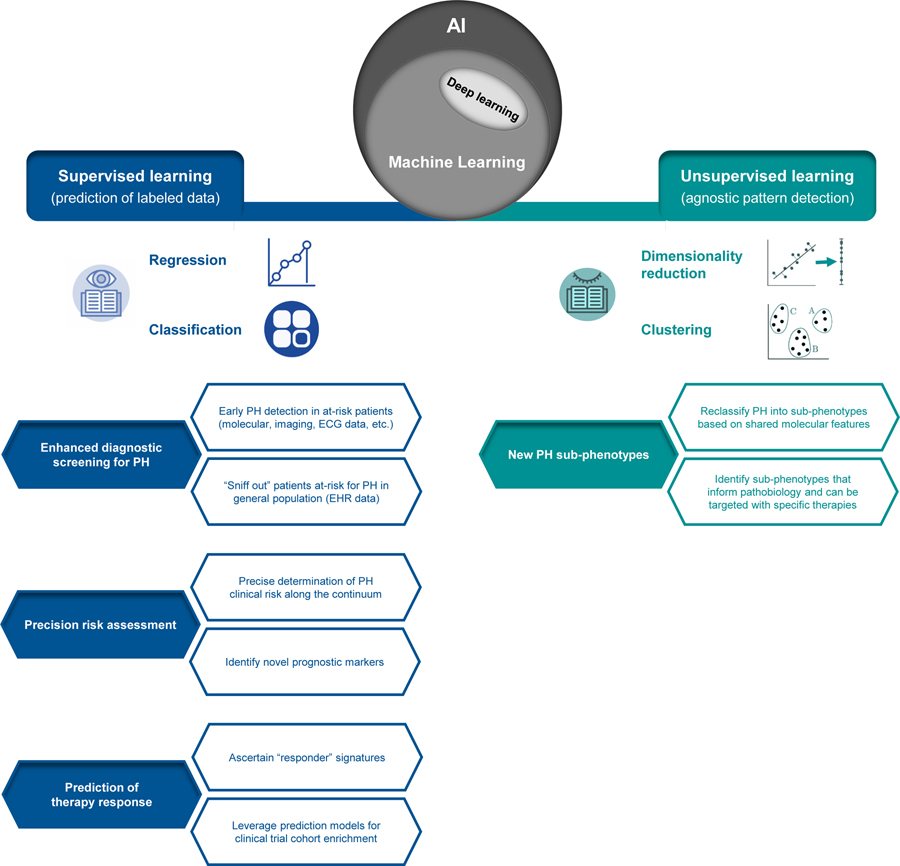
Figure 1. Overview of applied machine learning (ML) in pulmonary hypertension (PH).
Falling under the umbrella of artificial intelligence (AI), ML describes a family of algorithms used to make predictions or infer patterns in complex datasets. Supervised ML algorithms are trained to predict a known sample label (i.e. clinical feature or outcome), where a variety of data types can be input for prediction of a continuous or categorical feature (regression or classification). Unsupervised ML algorithms are most often applied for clustering, where patterns and structure are agnostically inferred in unlabeled datasets. Deep learning, an emerging sub-field of ML in which algorithms are built on artificial neural networks mimicking human brain connectivity, can be employed for supervised or unsupervised learning tasks. This figure summarizes potential high-yield applications of supervised and unsupervised ML methods in PH.