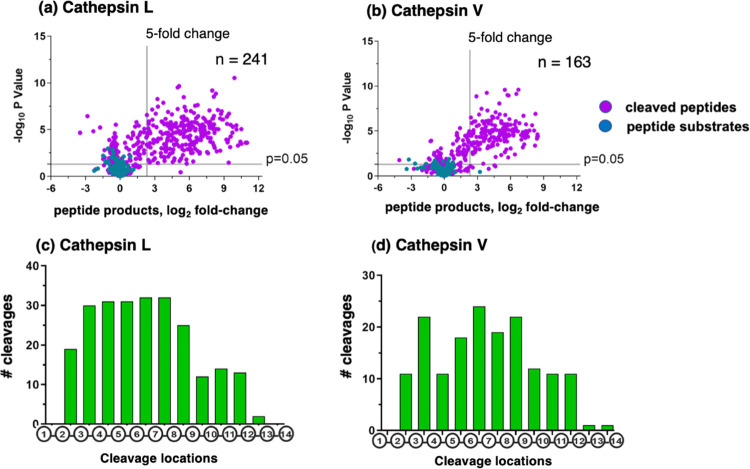
Figure 2.
Cathepsin L and cathepsin V peptide cleavage profiling analyzed by multiplex substrate profiling by mass spectrometry (MSP-MS). (a,b) Volcano plots of cleaved peptides generated by cathepsin L (a) and cathepsin V (b). The log2 ratios of relative quantities of peptide products generated by cathepsin L or cathepsin V (60 min incubation at pH 5.5) compared to no enzyme activity controls are illustrated with −log10p values. Peptide products generated with at least a 5-fold change above no enzyme activity controls and with p < 0.05 numbered 241 and 163 peptides in panels “a” and “b”, respectively, representing 8.1 and 7.9%, respectively, of the entire number of 2964 cleavage sites among the 228 peptides of the library. Peptide sequences were analyzed for the frequencies of amino acid residues at the P4–P4′ positions of the P1–↓P1′cleavage site. (c,d) Cleavage positions of 14-mer peptide substrates for cathepsin L (c) and cathepsin V (d). The number of cleavages by cathepsin L and cathepsin V at each of the peptide bonds of the 14-mer peptide substrates are illustrated.