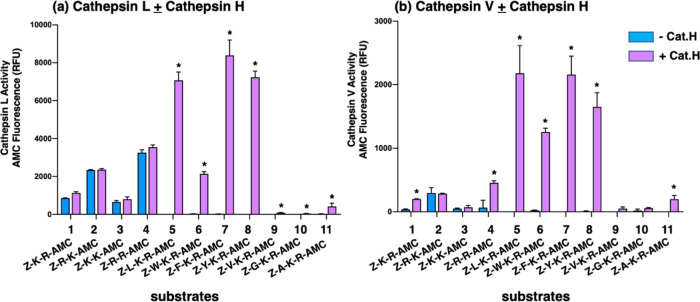
Figure 5.
Cathepsin L and cathepsin V cleavage specificities at dibasic residue sites assessed with variant dipeptide-AMC and tripeptide-AMC substrates. Cathepsin L (panel a) and cathepsin V (panel b) were evaluated for the cleavage of dipeptide-AMC substrates containing the four dibasic variant cleavage sites KR, RK, KK, and RR and compared to the cleavage of tripeptide-AMC substrates containing the K-R with adjacent hydrophobic residues (Leu, Trp, Phe, Tyr, Val) or nonpolar residues (Gly, Ala) at the N-terminal side of the dibasic K-R site. Cathepsin L and cathepsin V were incubated with each of these substrates at 37 °C for 60 min. Then, the aminopeptidase cathepsin H or control buffer was added and incubation continued at 37 °C for another 30 min to allow conversion of basic residue-extended AMC products to free AMC for fluorometric measurement (conducted as described in the Methods section, with example shown in the Supporting Information, Figure S1). Controls included incubation of cathepsin H alone with each of the substrates, which resulted in no fluorescence, indicating that cathepsin H does not remove the blocked N-terminal residues of Z-peptide-AMC substrates. Comparison of fluorescence observed in the absence and presence of cathepsin H is illustrated, with significant differences with p < 0.05 (student’s t-test, n = 3) indicated by asterisks.