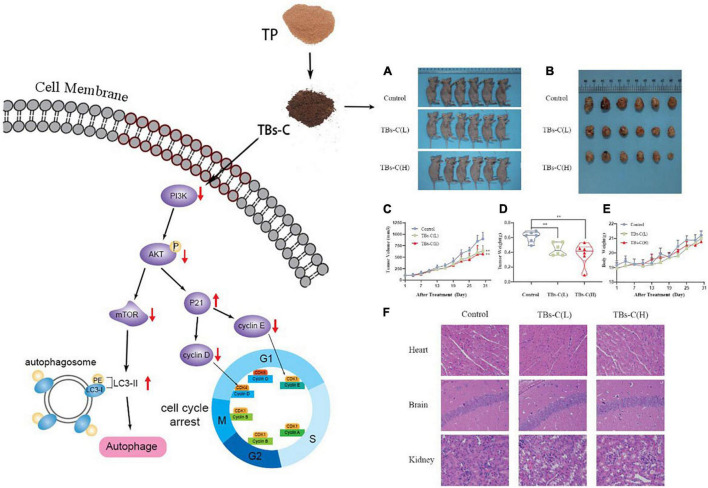
FIGURE 10.
Schematic diagram of TBs-C inhibiting human NSCLC cells in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, TBs-C is capable of increasing autophagic flux, inhibiting cell proliferation, enhancing apoptosis, and inducing G1 cell cycle arrest via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and AKT/p21 axis. In vivo, TBs-C enhances autophagy and inhibits tumor growth by downregulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway without causing cardiac, brain, or kidney toxicity.