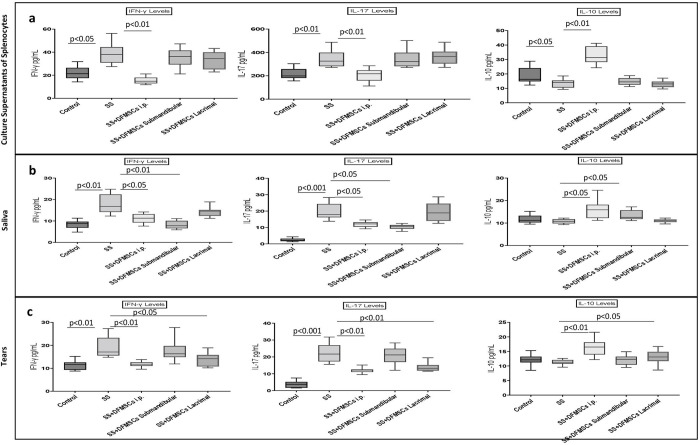
Fig 4. The secreted cytokine levels in the culture supernatant of splenocytes, saliva, and tears.
(a) The cytokine levels in the culture supernatants of splenocytes. Intraperitoneal injection of DFMSCs significantly increased IL-10 levels in Group 3a (p<0.01), and significantly decreased the secreted IFN-γ and IL-17 levels compared to Group 2 (p<0.01 and p<0.01, respectively). Submandibular and lacrimal injections of DFMSCs did not significantly change the secreted IFN-γ (p>0.05 and p>0.05, respectively), IL-17 (p>0.05 and p>0.05, respectively), and IL-10 levels when compared with Group 2 (p>0.05 and p>0.05, respectively). (b) The cytokine levels in saliva. Intraperitoneal injection of DFMSCs significantly increased IL-10 levels in Group 3a (p<0.05), and significantly decreased the secreted IFN-γ and IL-17 levels compared to Group 2 (p<0.05 and p<0.05, respectively). Submandibular injection of DFMSCs significantly decreased the secreted IFN-γ and IL-17 levels in the saliva compared to Group 2 (p<0.01 and p<0.05, respectively). Submandibular injection of DFMSCs significantly increased IL-10 levels in the saliva compared to Group 2 (p<0.05). (c) The cytokine levels in tears. Intraperitoneal injection of DFMSCs significantly increased IL-10 levels in Group 3a (p<0.05), and significantly decreased the secreted IFN-γ and IL-17 levels compared to Group 2 (p<0.01 and p<0.01, respectively). Lacrimal injection of DFMSCs significantly decreased the secreted IFN-γ and IL-17 levels in the tears compared to Group 2 (p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively). Lacrimal injection of DFMSCs significantly increased IL-10 levels in the saliva compared to Group 2 (p<0.05).