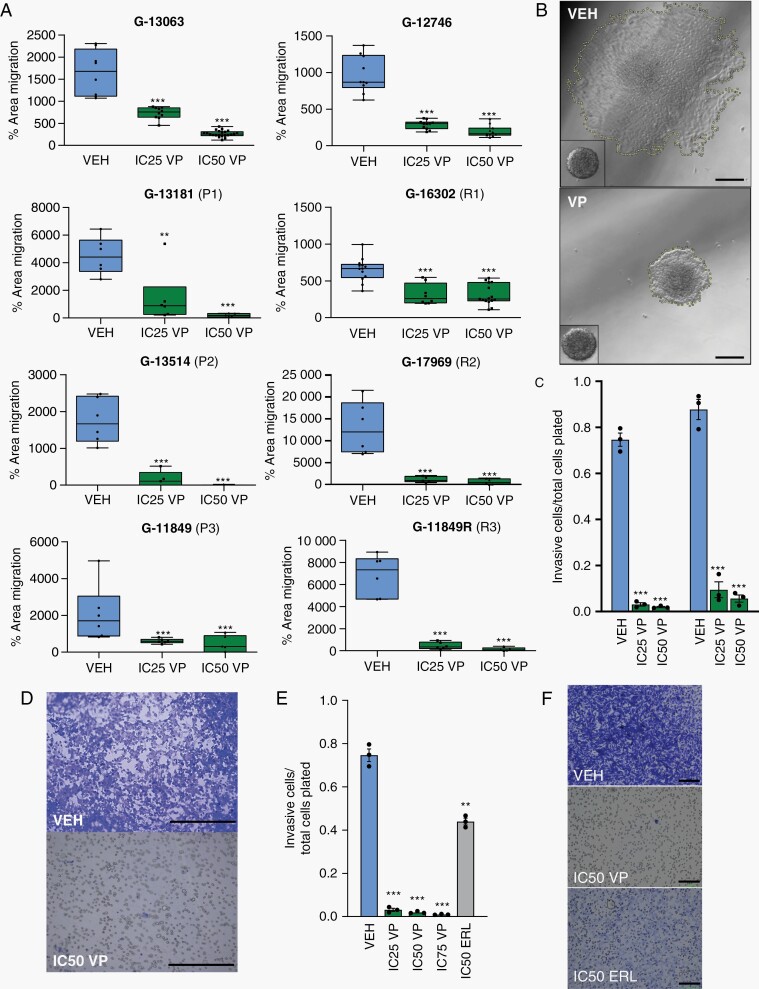
Fig. 2.
Verteporfin decreases tumor migration in vitro across primary and recurrent GBMs. (A) Dose-dependent effect of Verteporfin on spheroid dispersion/confluent cell migration, across 8 biologically distinct GBM lines, including 3 primary (P1-P3) and recurrent (R1-R3) pairs (n = 3 wells (dots) with multiple spheres/well, 2 independent experiments for G-13063 and G-16302; lines in box and whisker plots represent the mean spheroid area at 36 h after treatment, bars represent min/max). (B) Area of spheroid migration in representative G-13063 cells at 36 h of treatment with VEH or IC50 VP, marked by yellow dash line; inset shows spheroid at 1 h. Scale bars = 75 µm. (C) Dose-dependent effect of Verteporfin on transwell invasion. Dead cells are discarded prior to transwell plating and live cell number is measured using crystal violet (n = 3 wells (dots) per condition for each line). (D) Representative images of transwell membranes were analyzed in (C). Scale bars = 50 µm. (E) Identical transwell invasion assays to part (C) comparing effect of invasion in G-13063 cells treated with VEH, VP, or ERL (n = 3 wells (dots) per condition). (F) Representative images of transwell membranes from (E). Scale bars = 100 µm. (*P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 by Student t test; dose-dependence confirmed by ANOVA (P < .05); C, E: bars represent mean ± SEM). Abbreviations: ERL, Erlotinib; GBM, glioblastoma; VEH, vehicle; VP, Verteporfin.