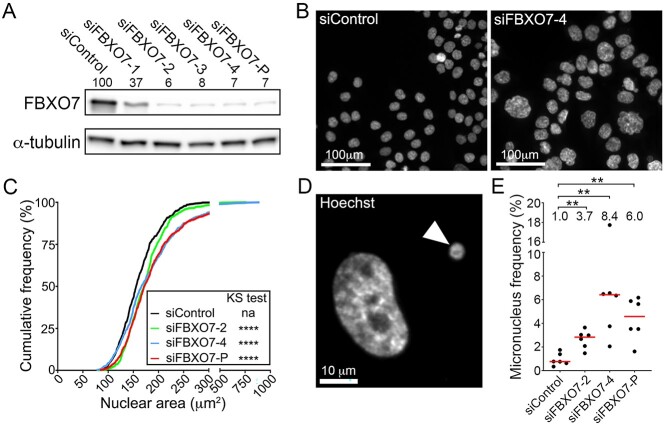
Figure 2.
FBXO7 silencing corresponds with increases in CIN-associated phenotypes in HCT116 cells. (A) Semi-quantitative western blot showing reduced FBXO7 expression relative to siControl in HCT116 cells following transfection with four individual (siFBXO7-1, -2, -3, -4) and pooled (siFBXO7-P) siRNAs. FBXO7 expression is normalized to the α-tubulin loading control and is presented relative to siControl (set to 100%). SiFBXO7-2 and -4 are the two most efficient individual siRNA duplexes. (N = 2). (B) Low-resolution images of Hoechst-stained nuclei showing striking visual increases in nuclear areas and cell-to-cell heterogeneity following FBXO7 silencing relative to siControl. (C) Graph showing statistically significant increases (i.e. rightward shift) in cumulative nuclear area distribution frequencies following FBXO7 silencing relative to siControl (two-sample KS test; na, not applicable; ****P-value < 0.0001). (N = 3, n = 6). (D) High-resolution image of a Hoechst-stained nucleus and micronucleus (arrowhead). (E) Dot plot identifies significant increases in frequencies of micronuclei following FBXO7 silencing relative to siControl. The median values are indicated by red bars, whereas the fold increases in the median values are presented below the statistical information (Mann-Whitney (MW) test; **P-value < 0.01; N = 3, n = 6).